This is page 1 of 16. Use http://codebase.md/mljar/mljar-supervised?page={x} to view the full context.
# Directory Structure
```
├── .github
│ └── workflows
│ ├── run-tests.yml
│ ├── test-installation-with-conda.yml
│ └── test-installation-with-pip-on-windows.yml
├── .gitignore
├── CITATION
├── examples
│ ├── notebooks
│ │ ├── basic_run.ipynb
│ │ └── Titanic.ipynb
│ └── scripts
│ ├── binary_classifier_adult_fairness.py
│ ├── binary_classifier_ensemble.py
│ ├── binary_classifier_marketing.py
│ ├── binary_classifier_random.py
│ ├── binary_classifier_Titanic.py
│ ├── binary_classifier.py
│ ├── multi_class_classifier_digits.py
│ ├── multi_class_classifier_MNIST.py
│ ├── multi_class_classifier.py
│ ├── multi_class_drug_fairness.py
│ ├── regression_acs_fairness.py
│ ├── regression_crime_fairness.py
│ ├── regression_housing_fairness.py
│ ├── regression_law_school_fairness.py
│ ├── regression.py
│ └── tabular_mar_2021.py
├── LICENSE
├── MANIFEST.in
├── pytest.ini
├── README.md
├── requirements_dev.txt
├── requirements.txt
├── setup.py
├── supervised
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── algorithms
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── algorithm.py
│ │ ├── baseline.py
│ │ ├── catboost.py
│ │ ├── decision_tree.py
│ │ ├── extra_trees.py
│ │ ├── factory.py
│ │ ├── knn.py
│ │ ├── lightgbm.py
│ │ ├── linear.py
│ │ ├── nn.py
│ │ ├── random_forest.py
│ │ ├── registry.py
│ │ ├── sklearn.py
│ │ └── xgboost.py
│ ├── automl.py
│ ├── base_automl.py
│ ├── callbacks
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── callback_list.py
│ │ ├── callback.py
│ │ ├── early_stopping.py
│ │ ├── learner_time_constraint.py
│ │ ├── max_iters_constraint.py
│ │ ├── metric_logger.py
│ │ ├── terminate_on_nan.py
│ │ └── total_time_constraint.py
│ ├── ensemble.py
│ ├── exceptions.py
│ ├── fairness
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── metrics.py
│ │ ├── optimization.py
│ │ ├── plots.py
│ │ ├── report.py
│ │ └── utils.py
│ ├── model_framework.py
│ ├── preprocessing
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── datetime_transformer.py
│ │ ├── encoding_selector.py
│ │ ├── exclude_missing_target.py
│ │ ├── goldenfeatures_transformer.py
│ │ ├── kmeans_transformer.py
│ │ ├── label_binarizer.py
│ │ ├── label_encoder.py
│ │ ├── preprocessing_categorical.py
│ │ ├── preprocessing_missing.py
│ │ ├── preprocessing_utils.py
│ │ ├── preprocessing.py
│ │ ├── scale.py
│ │ └── text_transformer.py
│ ├── tuner
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── data_info.py
│ │ ├── hill_climbing.py
│ │ ├── mljar_tuner.py
│ │ ├── optuna
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ ├── catboost.py
│ │ │ ├── extra_trees.py
│ │ │ ├── knn.py
│ │ │ ├── lightgbm.py
│ │ │ ├── nn.py
│ │ │ ├── random_forest.py
│ │ │ ├── tuner.py
│ │ │ └── xgboost.py
│ │ ├── preprocessing_tuner.py
│ │ ├── random_parameters.py
│ │ └── time_controller.py
│ ├── utils
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── additional_metrics.py
│ │ ├── additional_plots.py
│ │ ├── automl_plots.py
│ │ ├── common.py
│ │ ├── config.py
│ │ ├── constants.py
│ │ ├── data_validation.py
│ │ ├── importance.py
│ │ ├── jsonencoder.py
│ │ ├── leaderboard_plots.py
│ │ ├── learning_curves.py
│ │ ├── metric.py
│ │ ├── shap.py
│ │ ├── subsample.py
│ │ └── utils.py
│ └── validation
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── validation_step.py
│ ├── validator_base.py
│ ├── validator_custom.py
│ ├── validator_kfold.py
│ └── validator_split.py
└── tests
├── __init__.py
├── checks
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── check_automl_with_regression.py
│ ├── run_ml_tests.py
│ └── run_performance_tests.py
├── conftest.py
├── data
│ ├── 179.csv
│ ├── 24.csv
│ ├── 3.csv
│ ├── 31.csv
│ ├── 38.csv
│ ├── 44.csv
│ ├── 720.csv
│ ├── 737.csv
│ ├── acs_income_1k.csv
│ ├── adult_missing_values_missing_target_500rows.csv
│ ├── boston_housing.csv
│ ├── CrimeData
│ │ ├── cities.json
│ │ ├── crimedata.csv
│ │ └── README.md
│ ├── Drug
│ │ ├── Drug_Consumption.csv
│ │ └── README.md
│ ├── housing_regression_missing_values_missing_target.csv
│ ├── iris_classes_missing_values_missing_target.csv
│ ├── iris_missing_values_missing_target.csv
│ ├── LawSchool
│ │ ├── bar_pass_prediction.csv
│ │ └── README.md
│ ├── PortugeseBankMarketing
│ │ └── Data_FinalProject.csv
│ └── Titanic
│ ├── test_with_Survived.csv
│ └── train.csv
├── README.md
├── tests_algorithms
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── test_baseline.py
│ ├── test_catboost.py
│ ├── test_decision_tree.py
│ ├── test_extra_trees.py
│ ├── test_factory.py
│ ├── test_knn.py
│ ├── test_lightgbm.py
│ ├── test_linear.py
│ ├── test_nn.py
│ ├── test_random_forest.py
│ ├── test_registry.py
│ └── test_xgboost.py
├── tests_automl
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── test_adjust_validation.py
│ ├── test_automl_init.py
│ ├── test_automl_report.py
│ ├── test_automl_sample_weight.py
│ ├── test_automl_time_constraints.py
│ ├── test_automl.py
│ ├── test_data_types.py
│ ├── test_dir_change.py
│ ├── test_explain_levels.py
│ ├── test_golden_features.py
│ ├── test_handle_imbalance.py
│ ├── test_integration.py
│ ├── test_joblib_version.py
│ ├── test_models_needed_for_predict.py
│ ├── test_prediction_after_load.py
│ ├── test_repeated_validation.py
│ ├── test_restore.py
│ ├── test_stack_models_constraints.py
│ ├── test_targets.py
│ └── test_update_errors_report.py
├── tests_callbacks
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── test_total_time_constraint.py
├── tests_ensemble
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── test_save_load.py
├── tests_fairness
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── test_binary_classification.py
│ ├── test_multi_class_classification.py
│ └── test_regression.py
├── tests_preprocessing
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── disable_eda.py
│ ├── test_categorical_integers.py
│ ├── test_datetime_transformer.py
│ ├── test_encoding_selector.py
│ ├── test_exclude_missing.py
│ ├── test_goldenfeatures_transformer.py
│ ├── test_label_binarizer.py
│ ├── test_label_encoder.py
│ ├── test_preprocessing_missing.py
│ ├── test_preprocessing_utils.py
│ ├── test_preprocessing.py
│ ├── test_scale.py
│ └── test_text_transformer.py
├── tests_tuner
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── test_hill_climbing.py
│ ├── test_time_controller.py
│ └── test_tuner.py
├── tests_utils
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── test_compute_additional_metrics.py
│ ├── test_importance.py
│ ├── test_learning_curves.py
│ ├── test_metric.py
│ ├── test_shap.py
│ └── test_subsample.py
└── tests_validation
├── __init__.py
├── test_validator_kfold.py
└── test_validator_split.py
```
# Files
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```
AutoML_*
.vscode
# Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
__pycache__/
*.py[cod]
*$py.class
# C extensions
*.so
# Distribution / packaging
.Python
build/
develop-eggs/
dist/
downloads/
eggs/
.eggs/
lib/
lib64/
parts/
sdist/
var/
wheels/
*.egg-info/
.installed.cfg
*.egg
MANIFEST
# PyInstaller
# Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
# before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
*.manifest
*.spec
# Installer logs
pip-log.txt
pip-delete-this-directory.txt
# Unit test / coverage reports
htmlcov/
.tox/
.coverage
.coverage.*
.cache
nosetests.xml
coverage.xml
*.cover
.hypothesis/
.pytest_cache/
# Translations
*.mo
*.pot
# Django stuff:
*.log
local_settings.py
db.sqlite3
# Flask stuff:
instance/
.webassets-cache
# Scrapy stuff:
.scrapy
# Sphinx documentation
docs/_build/
# PyBuilder
target/
# Jupyter Notebook
.ipynb_checkpoints
# pyenv
.python-version
# celery beat schedule file
celerybeat-schedule
# SageMath parsed files
*.sage.py
# Environments
.env
.venv
env/
venv/
ENV/
env.bak/
venv.bak/
# Spyder project settings
.spyderproject
.spyproject
# Rope project settings
.ropeproject
# mkdocs documentation
/site
# mypy
.mypy_cache/
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/data/LawSchool/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```markdown
Source: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/danofer/law-school-admissions-bar-passage
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```markdown
# Running tests
To run all tests:
```
pytest tests -v -x
```
To run tests for `algorithms`:
```
pytest tests/tests_algorithms -v -x -s
```
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/data/CrimeData/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```markdown
Source: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/kkanda/communities%20and%20crime%20unnormalized%20data%20set?select=crimedata.csv
Description: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Communities%20and%20Crime%20Unnormalized
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/data/Drug/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```markdown
Source https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/obeykhadija/drug-consumptions-uci
Rating's for Drug Use:
CL0 Never Used
CL1 Used over a Decade Ago
CL2 Used in Last Decade
CL3 Used in Last Year 59
CL4 Used in Last Month
CL5 Used in Last Week
CL6 Used in Last Day
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```markdown
# MLJAR Automated Machine Learning for Humans
[](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised/actions/workflows/run-tests.yml)
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/mljar-supervised)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/mljar-supervised)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/mljar-supervised/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/mljar-supervised)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/mljar-supervised)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/mljar-supervised)
<p align="center">
<img
alt="mljar AutoML"
src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mljar/mljar-examples/master/media/AutoML_white.png#gh-light-mode-only" width="50%" />
</p>
<p align="center">
<img
alt="mljar AutoML"
src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mljar/mljar-examples/master/media/AutoML_black.png#gh-dark-mode-only" width="50%" />
</p>
---
**Documentation**: <a href="https://supervised.mljar.com/" target="_blank">https://supervised.mljar.com/</a>
**Source Code**: <a href="https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised" target="_blank">https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised</a>
**Looking for commercial support**: Please contact us by [email](https://mljar.com/contact/) for details
<p align="center">
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mljar/mljar-examples/master/media/pipeline_AutoML.png" width="100%" />
</p>
---
Watch full AutoML training in Python under 2 minutes. The training is done in [MLJAR Studio](https://mljar.com).
[](https://youtu.be/t_opxR5dbPU)
## Table of Contents
- [Automated Machine Learning](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#automated-machine-learning)
- [What's good in it?](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#whats-good-in-it)
- [AutoML Web App with GUI](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#automl-web-app-with-user-interface)
- [Automatic Documentation](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#automatic-documentation)
- [Available Modes](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#available-modes)
- [Fairness Aware Training](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#fairness-aware-training)
- [Examples](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#examples)
- [FAQ](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#faq)
- [Documentation](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#documentation)
- [Installation](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#installation)
- [Demo](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#demo)
- [Contributing](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#contributing)
- [Cite](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#cite)
- [License](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#license)
- [Commercial support](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#commercial-support)
- [MLJAR](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised#mljar)
# Automated Machine Learning
The `mljar-supervised` is an Automated Machine Learning Python package that works with tabular data. It is designed to save time for a data scientist. It abstracts the common way to preprocess the data, construct the machine learning models, and perform hyper-parameters tuning to find the best model :trophy:. It is no black box, as you can see exactly how the ML pipeline is constructed (with a detailed Markdown report for each ML model).
The `mljar-supervised` will help you with:
- explaining and understanding your data (Automatic Exploratory Data Analysis),
- trying many different machine learning models (Algorithm Selection and Hyper-Parameters tuning),
- creating Markdown reports from analysis with details about all models (Automatic-Documentation),
- saving, re-running, and loading the analysis and ML models.
It has four built-in modes of work:
- `Explain` mode, which is ideal for explaining and understanding the data, with many data explanations, like decision trees visualization, linear models coefficients display, permutation importance, and SHAP explanations of data,
- `Perform` for building ML pipelines to use in production,
- `Compete` mode that trains highly-tuned ML models with ensembling and stacking, with the purpose to use in ML competitions.
- `Optuna` mode can be used to search for highly-tuned ML models should be used when the performance is the most important, and computation time is not limited (it is available from version `0.10.0`)
Of course, you can further customize the details of each `mode` to meet the requirements.
## What's good in it?
- It uses many algorithms: `Baseline`, `Linear`, `Random Forest`, `Extra Trees`, `LightGBM`, `Xgboost`, `CatBoost`, `Neural Networks`, and `Nearest Neighbors`.
- It can compute Ensemble based on a greedy algorithm from [Caruana paper](http://www.cs.cornell.edu/~alexn/papers/shotgun.icml04.revised.rev2.pdf).
- It can stack models to build a level 2 ensemble (available in `Compete` mode or after setting the `stack_models` parameter).
- It can do features preprocessing, like missing values imputation and converting categoricals. What is more, it can also handle target values preprocessing.
- It can do advanced features engineering, like [Golden Features](https://supervised.mljar.com/features/golden_features/), [Features Selection](https://supervised.mljar.com/features/features_selection/), Text and Time Transformations.
- It can tune hyper-parameters with a `not-so-random-search` algorithm (random-search over a defined set of values) and hill climbing to fine-tune final models.
- It can compute the `Baseline` for your data so that you will know if you need Machine Learning or not!
- It has extensive explanations. This package is training simple `Decision Trees` with `max_depth <= 5`, so you can easily visualize them with amazing [dtreeviz](https://github.com/parrt/dtreeviz) to better understand your data.
- The `mljar-supervised` uses simple linear regression and includes its coefficients in the summary report, so you can check which features are used the most in the linear model.
- It cares about the explainability of models: for every algorithm, the feature importance is computed based on permutation. Additionally, for every algorithm, the SHAP explanations are computed: feature importance, dependence plots, and decision plots (explanations can be switched off with the `explain_level` parameter).
- There is automatic documentation for every ML experiment run with AutoML. The `mljar-supervised` creates markdown reports from AutoML training full of ML details, metrics, and charts.
<p align="center">
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mljar/visual-identity/main/media/infograph.png" width="100%" />
</p>
# AutoML Web App with User Interface
We created a Web App with GUI, so you don't need to write any code 🐍. Just upload your data. Please check the Web App at [github.com/mljar/automl-app](https://github.com/mljar/automl-app). You can run this Web App locally on your computer, so your data is safe and secure :cat:
<kbd>
<img src="https://github.com/mljar/automl-app/blob/main/media/web-app.gif" alt="AutoML training in Web App"></img>
</kbd>
# Automatic Documentation
## The AutoML Report
The report from running AutoML will contain the table with information about each model score and the time needed to train the model. There is a link for each model, which you can click to see the model's details. The performance of all ML models is presented as scatter and box plots so you can visually inspect which algorithms perform the best :trophy:.

## The `Decision Tree` Report
The example for `Decision Tree` summary with trees visualization. For classification tasks, additional metrics are provided:
- confusion matrix
- threshold (optimized in the case of binary classification task)
- F1 score
- Accuracy
- Precision, Recall, MCC

## The `LightGBM` Report
The example for `LightGBM` summary:

## Available Modes
In the [docs](https://supervised.mljar.com/features/modes/) you can find details about AutoML modes that are presented in the table.
<p align="center">
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mljar/visual-identity/main/media/mljar_modes.png" width="100%" />
</p>
### Explain
```py
automl = AutoML(mode="Explain")
```
It is aimed to be used when the user wants to explain and understand the data.
- It is using 75%/25% train/test split.
- It uses: `Baseline`, `Linear`, `Decision Tree`, `Random Forest`, `Xgboost`, `Neural Network' algorithms, and ensemble.
- It has full explanations: learning curves, importance plots, and SHAP plots.
### Perform
```py
automl = AutoML(mode="Perform")
```
It should be used when the user wants to train a model that will be used in real-life use cases.
- It uses a 5-fold CV.
- It uses: `Linear`, `Random Forest`, `LightGBM`, `Xgboost`, `CatBoost`, and `Neural Network`. It uses ensembling.
- It has learning curves and importance plots in reports.
### Compete
```py
automl = AutoML(mode="Compete")
```
It should be used for machine learning competitions.
- It adapts the validation strategy depending on dataset size and `total_time_limit`. It can be: a train/test split (80/20), 5-fold CV or 10-fold CV.
- It is using: `Linear`, `Decision Tree`, `Random Forest`, `Extra Trees`, `LightGBM`, `Xgboost`, `CatBoost`, `Neural Network`, and `Nearest Neighbors`. It uses ensemble and **stacking**.
- It has only learning curves in the reports.
### Optuna
```py
automl = AutoML(mode="Optuna", optuna_time_budget=3600)
```
It should be used when the performance is the most important and time is not limited.
- It uses a 10-fold CV
- It uses: `Random Forest`, `Extra Trees`, `LightGBM`, `Xgboost`, and `CatBoost`. Those algorithms are tuned by `Optuna` framework for `optuna_time_budget` seconds, each. Algorithms are tuned with original data, without advanced feature engineering.
- It uses advanced feature engineering, stacking and ensembling. The hyperparameters found for original data are reused with those steps.
- It produces learning curves in the reports.
## How to save and load AutoML?
All models in the AutoML are saved and loaded automatically. No need to call `save()` or `load()`.
### Example:
#### Train AutoML
```python
automl = AutoML(results_path="AutoML_classifier")
automl.fit(X, y)
```
You will have all models saved in the `AutoML_classifier` directory. Each model will have a separate directory with the `README.md` file with all details from the training.
#### Compute predictions
```python
automl = AutoML(results_path="AutoML_classifier")
automl.predict(X)
```
The AutoML automatically loads models from the `results_path` directory. If you will call `fit()` on already trained AutoML then you will get a warning message that AutoML is already fitted.
### Why do you automatically save all models?
All models are automatically saved to be able to restore the training after interruption. For example, you are training AutoML for 48 hours, and after 47 hours, there is some unexpected interruption. In MLJAR AutoML you just call the same training code after the interruption and AutoML reloads already trained models and finishes the training.
## Supported evaluation metrics (`eval_metric` argument in `AutoML()`)
- for binary classification: `logloss`, `auc`, `f1`, `average_precision`, `accuracy`- default is `logloss`
- for multiclass classification: `logloss`, `f1`, `accuracy` - default is `logloss`
- for regression: `rmse`, `mse`, `mae`, `r2`, `mape`, `spearman`, `pearson` - default is `rmse`
If you don't find the `eval_metric` that you need, please add a new issue. We will add it.
## Fairness Aware Training
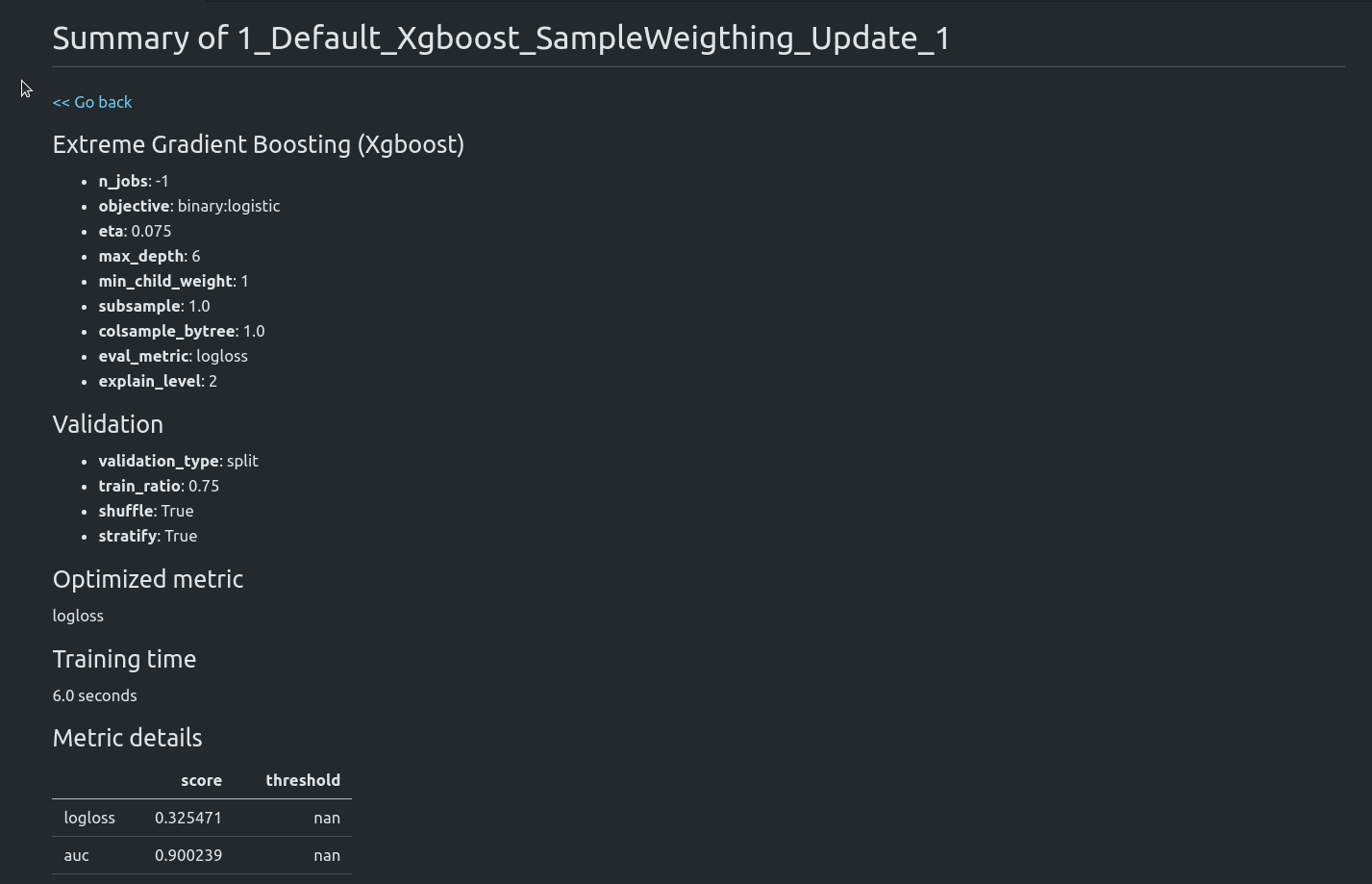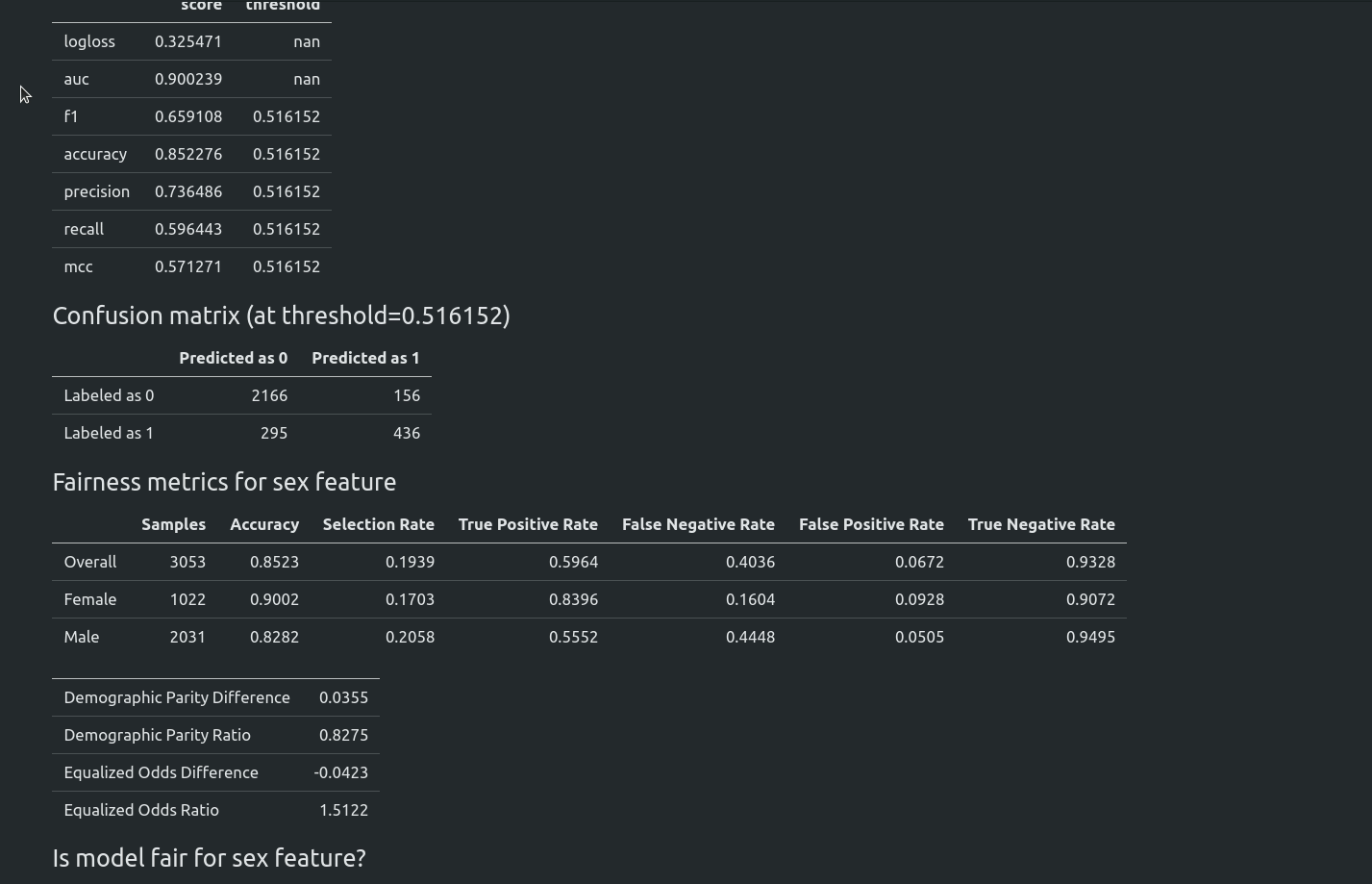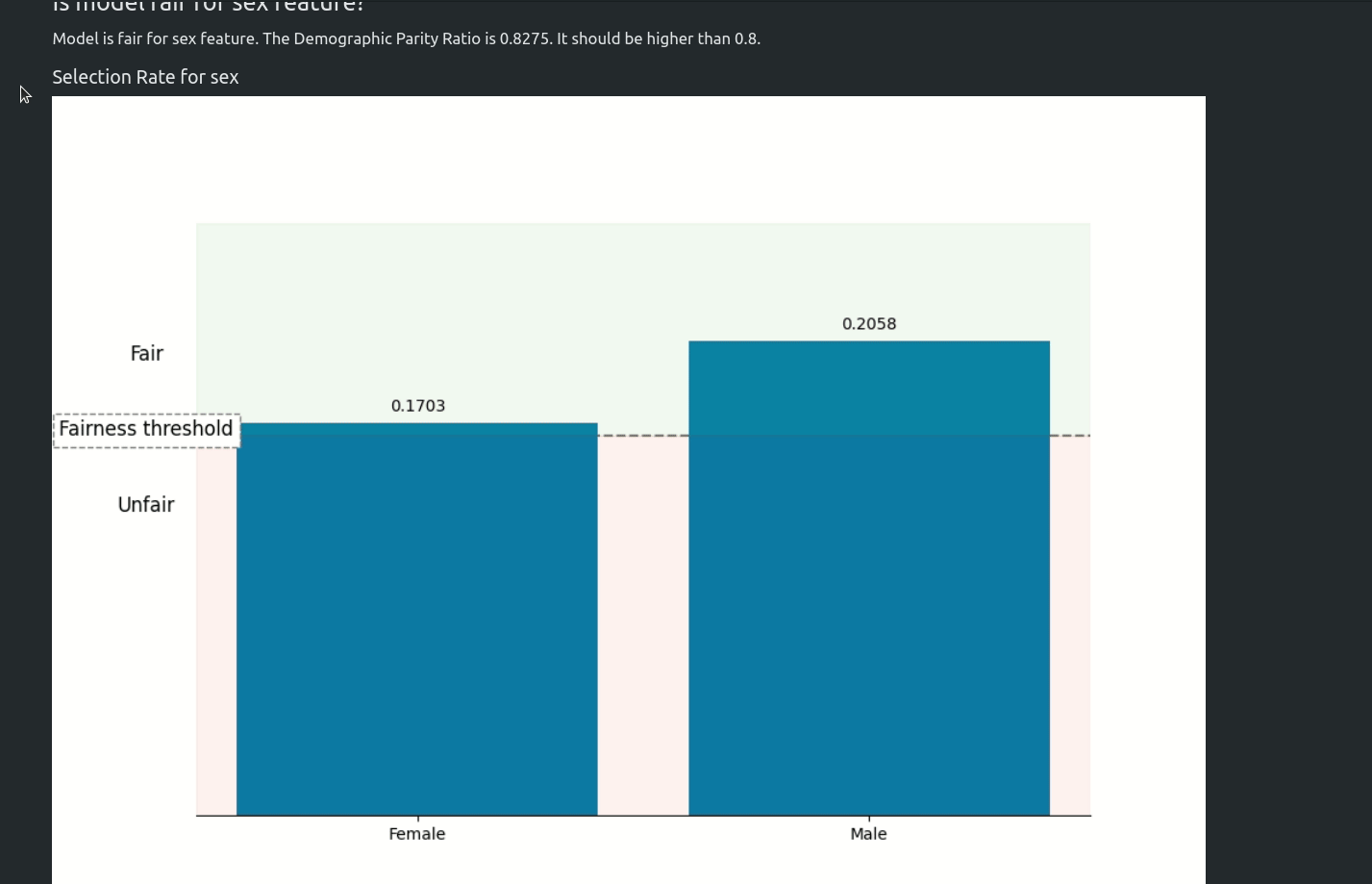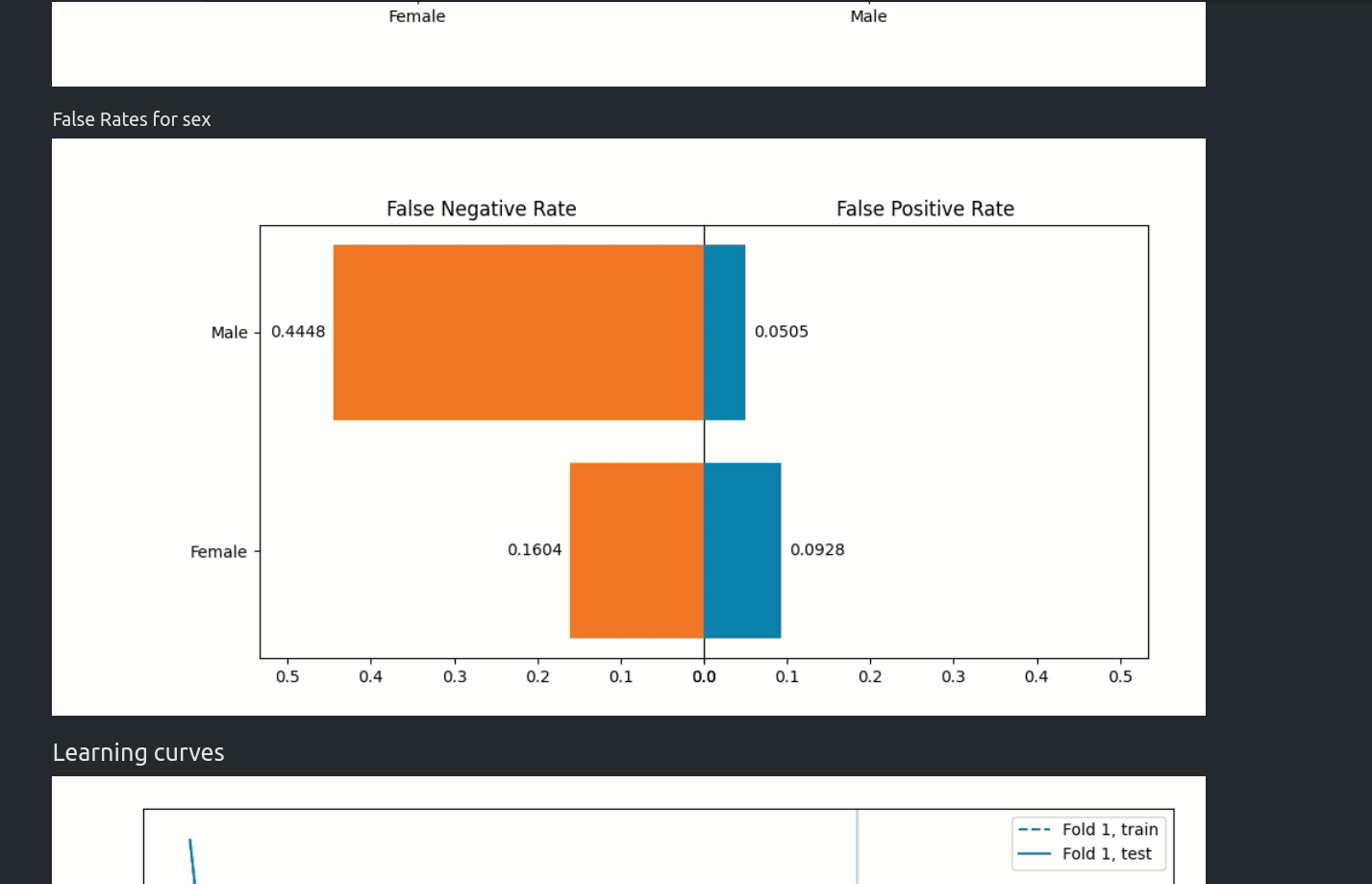
Starting from version `1.0.0` AutoML can optimize the Machine Learning pipeline with sensitive features. There are the following fairness related arguments in the AutoML constructor:
- `fairness_metric` - metric which will be used to decide if the model is fair,
- `fairness_threshold` - threshold used in decision about model fairness,
- `privileged_groups` - privileged groups used in fairness metrics computation,
- `underprivileged_groups` - underprivileged groups used in fairness metrics computation.
The `fit()` method accepts `sensitive_features`. When sensitive features are passed to AutoML, the best model will be selected among fair models only. In the AutoML reports, additional information about fairness metrics will be added. The MLJAR AutoML supports two methods for bias mitigation:
- Sample Weighting - assigns weights to samples to treat samples equally,
- Smart Grid Search - similar to Sample Weighting, where different weights are checked to optimize fairness metric.
The fair ML building can be used with all algorithms, including `Ensemble` and `Stacked Ensemble`. We support three Machine Learning tasks:
- binary classification,
- mutliclass classification,
- regression.
Example code:
```python
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
from supervised.automl import AutoML
data = fetch_openml(data_id=1590, as_frame=True)
X = data.data
y = (data.target == ">50K") * 1
sensitive_features = X[["sex"]]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, S_train, S_test = train_test_split(
X, y, sensitive_features, stratify=y, test_size=0.75, random_state=42
)
automl = AutoML(
algorithms=[
"Xgboost"
],
train_ensemble=False,
fairness_metric="demographic_parity_ratio",
fairness_threshold=0.8,
privileged_groups = [{"sex": "Male"}],
underprivileged_groups = [{"sex": "Female"}],
)
automl.fit(X_train, y_train, sensitive_features=S_train)
```
You can read more about fairness aware AutoML training in our article https://mljar.com/blog/fairness-machine-learning/
# Examples
## :point_right: Binary Classification Example
There is a simple interface available with `fit` and `predict` methods.
```python
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from supervised.automl import AutoML
df = pd.read_csv(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pplonski/datasets-for-start/master/adult/data.csv",
skipinitialspace=True,
)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
df[df.columns[:-1]], df["income"], test_size=0.25
)
automl = AutoML()
automl.fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = automl.predict(X_test)
```
AutoML `fit` will print:
```py
Create directory AutoML_1
AutoML task to be solved: binary_classification
AutoML will use algorithms: ['Baseline', 'Linear', 'Decision Tree', 'Random Forest', 'Xgboost', 'Neural Network']
AutoML will optimize for metric: logloss
1_Baseline final logloss 0.5519845471086654 time 0.08 seconds
2_DecisionTree final logloss 0.3655910192804364 time 10.28 seconds
3_Linear final logloss 0.38139916864708445 time 3.19 seconds
4_Default_RandomForest final logloss 0.2975204390214936 time 79.19 seconds
5_Default_Xgboost final logloss 0.2731086827200411 time 5.17 seconds
6_Default_NeuralNetwork final logloss 0.319812276905242 time 21.19 seconds
Ensemble final logloss 0.2731086821194617 time 1.43 seconds
```
- the AutoML results in [Markdown report](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-examples/tree/master/Income_classification/AutoML_1#automl-leaderboard)
- the Xgboost [Markdown report](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-examples/blob/master/Income_classification/AutoML_1/5_Default_Xgboost/README.md), please take a look at amazing dependence plots produced by SHAP package :sparkling_heart:
- the Decision Tree [Markdown report](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-examples/blob/master/Income_classification/AutoML_1/2_DecisionTree/README.md), please take a look at beautiful tree visualization :sparkles:
- the Logistic Regression [Markdown report](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-examples/blob/master/Income_classification/AutoML_1/3_Linear/README.md), please take a look at coefficients table, and you can compare the SHAP plots between (Xgboost, Decision Tree and Logistic Regression) :coffee:
## :point_right: Multi-Class Classification Example
The example code for classification of the optical recognition of handwritten digits dataset. Running this code in less than 30 minutes will result in test accuracy ~98%.
```python
import pandas as pd
# scikit learn utilites
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# mljar-supervised package
from supervised.automl import AutoML
# load the data
digits = load_digits()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
pd.DataFrame(digits.data), digits.target, stratify=digits.target, test_size=0.25,
random_state=123
)
# train models with AutoML
automl = AutoML(mode="Perform")
automl.fit(X_train, y_train)
# compute the accuracy on test data
predictions = automl.predict_all(X_test)
print(predictions.head())
print("Test accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, predictions["label"].astype(int)))
```
## :point_right: Regression Example
Regression example on `California Housing` house prices data.
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from supervised.automl import AutoML # mljar-supervised
# Load the data
housing = fetch_california_housing()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
pd.DataFrame(housing.data, columns=housing.feature_names),
housing.target,
test_size=0.25,
random_state=123,
)
# train models with AutoML
automl = AutoML(mode="Explain")
automl.fit(X_train, y_train)
# compute the MSE on test data
predictions = automl.predict(X_test)
print("Test MSE:", mean_squared_error(y_test, predictions))
```
## :point_right: More Examples
- [**Income classification**](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-examples/tree/master/Income_classification) - it is a binary classification task on census data
- [**Iris classification**](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-examples/tree/master/Iris_classification) - it is a multiclass classification on Iris flowers data
- [**House price regression**](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-examples/tree/master/House_price_regression) - it is a regression task on Boston houses data
# FAQ
<details><summary>What method is used for hyperparameters optimization?</summary>
- For modes: `Explain`, `Perform`, and `Compete` there is used a random search method combined with hill climbing. In this approach, all checked models are saved and used for building Ensemble.
- For mode: `Optuna` the Optuna framework is used. It uses using TPE sampler for tuning. Models checked during the Optuna hyperparameters search are not saved, only the best model is saved (the final model from tuning). You can check the details about checked hyperparameters from optuna by checking study files in the `optuna` directory in your AutoML `results_path`.
</details>
<details><summary>How to save and load AutoML?</summary>
The save and load of AutoML models is automatic. All models created during AutoML training are saved in the directory set in `results_path` (argument of `AutoML()` constructor). If there is no `results_path` set, then the directory is created based on following name convention: `AutoML_{number}` the `number` will be number from 1 to 1000 (depends which directory name will be free).
Example save and load:
```python
automl = AutoML(results_path='AutoML_1')
automl.fit(X, y)
```
The all models from AutoML are saved in `AutoML_1` directory.
To load models:
```python
automl = AutoML(results_path='AutoML_1')
automl.predict(X)
```
</details>
<details><summary>How to set ML task (select between classification or regression)?</summary>
The MLJAR AutoML can work with:
- binary classification
- multi-class classification
- regression
The ML task detection is automatic based on target values. There can be situation if you want to manually force AutoML to select the ML task, then you need to set `ml_task` parameter. It can be set to `'binary_classification'`, `'multiclass_classification'`, `'regression'`.
Example:
```python
automl = AutoML(ml_task='regression')
automl.fit(X, y)
```
In the above example the regression model will be fitted.
</details>
<details><summary>How to reuse Optuna hyperparameters?</summary>
You can reuse Optuna hyperparameters that were found in other AutoML training. You need to pass them in `optuna_init_params` argument. All hyperparameters found during Optuna tuning are saved in the `optuna/optuna.json` file (inside `results_path` directory).
Example:
```python
optuna_init = json.loads(open('previous_AutoML_training/optuna/optuna.json').read())
automl = AutoML(
mode='Optuna',
optuna_init_params=optuna_init
)
automl.fit(X, y)
```
When reusing Optuna hyperparameters the Optuna tuning is simply skipped. The model will be trained with hyperparameters set in `optuna_init_params`. Right now there is no option to continue Optuna tuning with seed parameters.
</details>
<details><summary>How to know the order of classes for binary or multiclass problem when using predict_proba?</summary>
To get predicted probabilites with information about class label please use the `predict_all()` method. It returns the pandas DataFrame with class names in the columns. The order of predicted columns is the same in the `predict_proba()` and `predict_all()` methods. The `predict_all()` method will additionaly have the column with the predicted class label.
</details>
# Documentation
For details please check [mljar-supervised docs](https://supervised.mljar.com).
# Installation
From PyPi repository:
```
pip install mljar-supervised
```
To install this package with conda run:
```
conda install -c conda-forge mljar-supervised
```
From source code:
```
git clone https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised.git
cd mljar-supervised
python setup.py install
```
Installation for development
```
git clone https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised.git
virtualenv venv --python=python3.6
source venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install -r requirements_dev.txt
```
Running in the docker:
```
FROM python:3.7-slim-buster
RUN apt-get update && apt-get -y update
RUN apt-get install -y build-essential python3-pip python3-dev
RUN pip3 -q install pip --upgrade
RUN pip3 install mljar-supervised jupyter
CMD ["jupyter", "notebook", "--port=8888", "--no-browser", "--ip=0.0.0.0", "--allow-root"]
```
Install from GitHub with pip:
```
pip install -q -U git+https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised.git@master
```
# Demo
In the below demo GIF you will see:
- MLJAR AutoML trained in Jupyter Notebook on the Titanic dataset
- overview of created files
- a showcase of selected plots created during AutoML training
- algorithm comparison report along with their plots
- example of README file and CSV file with results

# Contributing
To get started take a look at our [Contribution Guide](https://supervised.mljar.com/contributing/) for information about our process and where you can fit in!
### Contributors
<a href="https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised/graphs/contributors">
<img src="https://contributors-img.web.app/image?repo=mljar/mljar-supervised" />
</a>
# Cite
Would you like to cite MLJAR? Great! :)
You can cite MLJAR as follows:
```
@misc{mljar,
author = {Aleksandra P\l{}o\'{n}ska and Piotr P\l{}o\'{n}ski},
year = {2021},
publisher = {MLJAR},
address = {\L{}apy, Poland},
title = {MLJAR: State-of-the-art Automated Machine Learning Framework for Tabular Data. Version 0.10.3},
url = {https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised}
}
```
Would love to hear from you about how have you used MLJAR AutoML in your project.
Please feel free to let us know at

# License
The `mljar-supervised` is provided with [MIT license](https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised/blob/master/LICENSE).
# Commercial support
Looking for commercial support? Do you need new feature implementation? Please contact us by [email](https://mljar.com/contact/) for details.
# MLJAR
<p align="center">
<img src="https://github.com/mljar/mljar-examples/blob/master/media/large_logo.png" width="314" />
</p>
The `mljar-supervised` is an open-source project created by [MLJAR](https://mljar.com). We care about ease of use in Machine Learning.
The [mljar.com](https://mljar.com) provides a beautiful and simple user interface for building machine learning models.
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/algorithms/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/callbacks/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/fairness/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/preprocessing/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/tuner/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/tuner/optuna/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/validation/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/checks/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_algorithms/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_callbacks/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_ensemble/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_fairness/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_preprocessing/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_tuner/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_validation/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pytest.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```
[pytest]
addopts = -p no:warnings
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements_dev.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```
pytest
black
pytest-cov
coveralls
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
__version__ = "1.1.18"
from supervised.automl import AutoML
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/checks/run_performance_tests.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
from tests.tests_bin_class.test_performance import *
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/checks/run_ml_tests.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
from tests.tests_bin_class.run import *
from tests.tests_multi_class.run import *
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/utils/constants.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
# tasks that can be handled by the package
BINARY_CLASSIFICATION = "binary_classification"
MULTICLASS_CLASSIFICATION = "multiclass_classification"
REGRESSION = "regression"
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/conftest.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
from pathlib import Path
import pytest
@pytest.fixture
def data_folder(request) -> Path:
folder_path = Path(__file__).parent / 'data'
assert folder_path.exists()
request.cls.data_folder = folder_path
return folder_path
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import json
from supervised.utils.jsonencoder import MLJSONEncoder
def json_loads(data, *args, **kwargs):
return json.loads(data, *args, **kwargs)
def json_dumps(data, *args, **kwargs):
return json.dumps(data, cls=MLJSONEncoder, *args, **kwargs)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/validation/validator_base.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class BaseValidator(object):
def __init__(self, params):
self.params = params
def split(self):
pass
def get_n_splits(self):
pass
def get_repeats(self):
return 1
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```
numpy>=1.19.5,<2
pandas>=2.0.0
scipy>=1.6.1
scikit-learn>=1.5.0
xgboost>=2.0.0
lightgbm>=3.0.0
catboost>=0.24.4
joblib>=1.0.1
tabulate>=0.8.7
matplotlib>=3.2.2
dtreeviz>=2.2.2
shap>=0.42.1
seaborn>=0.11.1
optuna-integration>=3.6.0
mljar-scikit-plot>=0.3.11
markdown
typing-extensions
ipython
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/regression.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.automl import AutoML
df = pd.read_csv("./tests/data/housing_regression_missing_values_missing_target.csv")
x_cols = [c for c in df.columns if c != "MEDV"]
X = df[x_cols]
y = df["MEDV"]
automl = AutoML()
automl.fit(X, y)
df["predictions"] = automl.predict(X)
print("Predictions")
print(df[["MEDV", "predictions"]].head())
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/utils/subsample.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from supervised.algorithms.registry import REGRESSION
def subsample(X, y, ml_task, train_size):
shuffle = True
stratify = None
if ml_task != REGRESSION:
stratify = y
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, train_size=train_size, shuffle=shuffle, stratify=stratify
)
return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/regression_law_school_fairness.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.automl import AutoML
df = pd.read_csv("tests/data/LawSchool/bar_pass_prediction.csv")
df["race1"][df["race1"] != "white"] = "non-white" # keep it as binary feature
X = df[["gender", "lsat", "race1", "pass_bar"]]
y = df["gpa"]
sensitive_features = df["race1"]
automl = AutoML(
algorithms=["Xgboost", "LightGBM", "Extra Trees"],
train_ensemble=True,
fairness_threshold=0.9,
)
automl.fit(X, y, sensitive_features=sensitive_features)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/utils/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
LOG_LEVEL = logging.ERROR
# from guppy import hpy
# from pympler import summary
# from pympler import muppy
import time
import numpy as np
def mem(msg=""):
"""Memory usage in MB"""
time.sleep(5)
with open("/proc/self/status") as f:
memusage = f.read().split("VmRSS:")[1].split("\n")[0][:-3]
print(msg, "- memory:", np.round(float(memusage.strip()) / 1024.0), "MB")
# all_objects = muppy.get_objects()
# sum1 = summary.summarize(all_objects)
# summary.print_(sum1)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/exceptions.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
from supervised.utils.config import LOG_LEVEL
logging.basicConfig(
format="%(asctime)s %(name)s %(levelname)s %(message)s", level=logging.ERROR
)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.setLevel(LOG_LEVEL)
class AutoMLException(Exception):
def __init__(self, message):
super(AutoMLException, self).__init__(message)
logger.error(message)
class NotTrainedException(Exception):
def __init__(self, message):
super(NotTrainedException, self).__init__(message)
logger.debug(message)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/tuner/random_parameters.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
class RandomParameters:
"""
Example params are in JSON format:
{
"booster": ["gbtree", "gblinear"],
"objective": ["binary:logistic"],
"eval_metric": ["auc", "logloss"],
"eta": [0.0025, 0.005, 0.0075, 0.01, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1]
}
"""
@staticmethod
def get(params, seed=1):
np.random.seed(seed)
generated_params = {"seed": seed}
for k in params:
generated_params[k] = np.random.permutation(params[k])[0].item()
return generated_params
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/callbacks/max_iters_constraint.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
from supervised.callbacks.callback import Callback
class MaxItersConstraint(Callback):
def __init__(self, params):
super(MaxItersConstraint, self).__init__(params)
self.name = params.get("name", "max_iters_constraint")
self.max_iters = params.get("max_iters", 10)
def add_and_set_learner(self, learner):
self.learner = learner
def on_iteration_end(self, logs, predictions):
# iters are computed starting from 0
if logs.get("iter_cnt") + 1 >= self.max_iters:
self.learner.stop_training = True
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_algorithms/test_registry.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
from supervised.algorithms.registry import AlgorithmsRegistry
class AlgorithmsRegistryTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_add_to_registry(self):
class Model1:
algorithm_short_name = ""
model1 = {
"task_name": "binary_classification",
"model_class": Model1,
"model_params": {},
"required_preprocessing": {},
"additional": {},
"default_params": {},
}
AlgorithmsRegistry.add(**model1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_algorithms/test_factory.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
from supervised.algorithms.factory import AlgorithmFactory
from supervised.algorithms.xgboost import XgbAlgorithm
class AlgorithmFactoryTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_fit(self):
params = {
"learner_type": "Xgboost",
"objective": "binary:logistic",
"eval_metric": "logloss",
}
learner = AlgorithmFactory.get_algorithm(params)
self.assertEqual(
learner.algorithm_short_name, XgbAlgorithm.algorithm_short_name
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/utils/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import copy
class Store:
data = {}
def set(self, key, value):
Store.data[key] = value
def get(self, key):
return copy.deepcopy(Store.data[key])
def dump_data(file_path, df):
store = Store()
store.set(file_path, df)
# try:
# df.to_parquet(file_path, index=False)
# except Exception as e:
# df.to_csv(file_path, index=False)
def load_data(file_path):
store = Store()
return store.get(file_path)
# try:
# return pd.read_parquet(file_path)
# except Exception as e:
# return pd.read_csv(file_path)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/callbacks/callback.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
class Callback(object):
def __init__(self, params):
self.params = params
self.learners = []
self.learner = None # current learner
self.name = "callback"
def add_and_set_learner(self, learner):
self.learners += [learner]
self.learner = learner
def on_learner_train_start(self, logs):
pass
def on_learner_train_end(self, logs):
pass
def on_iteration_start(self, logs):
pass
def on_iteration_end(self, logs, predictions):
pass
def on_framework_train_end(self, logs):
pass
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_tuner/test_tuner.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
from supervised.tuner.mljar_tuner import MljarTuner
class TunerTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_key_params(self):
params1 = {
"preprocessing": {"p1": 1, "p2": 2},
"learner": {"p1": 1, "p2": 2},
"validation_strategy": {},
}
params2 = {
"preprocessing": {"p1": 1, "p2": 2},
"learner": {"p2": 2, "p1": 1},
"validation_strategy": {},
}
key1 = MljarTuner.get_params_key(params1)
key2 = MljarTuner.get_params_key(params2)
self.assertEqual(key1, key2)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/multi_class_classifier.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from supervised.automl import AutoML
import supervised
import warnings
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from supervised import AutoML
from supervised.exceptions import AutoMLException
df = pd.read_csv("tests/data/iris_missing_values_missing_target.csv")
X = df[["feature_1", "feature_2", "feature_3", "feature_4"]]
y = df["class"]
automl = AutoML()
automl.fit(X, y)
predictions = automl.predict_all(X)
print(predictions.head())
print(predictions.tail())
print(X.shape)
print(predictions.shape)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/regression_crime_fairness.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.automl import AutoML
# data source http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Communities%20and%20Crime%20Unnormalized
df = pd.read_csv("tests/data/CrimeData/crimedata.csv", na_values=["?"])
X = df[df.columns[5:129]]
y = df["ViolentCrimesPerPop"]
sensitive_features = (df["racePctWhite"] > 84).astype(str)
automl = AutoML(
#algorithms=["Decision Tree", "Neural Network", "Xgboost", "Linear", "CatBoost"],
algorithms=["Xgboost", "Linear", "CatBoost"],
train_ensemble=True,
fairness_threshold=0.5,
)
automl.fit(X, y, sensitive_features=sensitive_features)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/binary_classifier_Titanic.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from supervised import AutoML
train = pd.read_csv(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pplonski/datasets-for-start/master/Titanic/train.csv"
)
print(train.head())
X = train[train.columns[2:]]
y = train["Survived"]
automl = AutoML() # default mode is Explain
automl.fit(X, y)
test = pd.read_csv(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pplonski/datasets-for-start/master/Titanic/test_with_Survived.csv"
)
predictions = automl.predict(test)
print(predictions)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy_score(test['Survived'], predictions)*100.0:.2f}%")
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/regression_housing_fairness.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.automl import AutoML
df = pd.read_csv("./tests/data/boston_housing.csv")
x_cols = [c for c in df.columns if c != "MEDV"]
df["large_B"] = (df["B"] > 380) * 1
df["large_B"] = df["large_B"].astype(str)
print(df["large_B"].dtype.name)
sensitive_features = df["large_B"]
X = df[x_cols]
y = df["MEDV"]
automl = AutoML(
algorithms=["Xgboost", "LightGBM"],
train_ensemble=True,
fairness_threshold=0.9,
)
automl.fit(X, y, sensitive_features=sensitive_features)
df["predictions"] = automl.predict(X)
print("Predictions")
print(df[["MEDV", "predictions"]].head())
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_preprocessing/test_encoding_selector.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import pandas as pd
from supervised.preprocessing.encoding_selector import EncodingSelector
from supervised.preprocessing.preprocessing_categorical import PreprocessingCategorical
class CategoricalIntegersTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_selector(self):
d = {"col1": [f"{i}" for i in range(31)], "col2": ["a"] * 31}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
self.assertEqual(
EncodingSelector.get(df, None, "col1"),
PreprocessingCategorical.MANY_CATEGORIES,
)
self.assertEqual(
EncodingSelector.get(df, None, "col2"),
PreprocessingCategorical.FEW_CATEGORIES,
)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/binary_classifier_marketing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import pandas as pd
from supervised.automl import AutoML
import os
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
df = pd.read_csv("tests/data/PortugeseBankMarketing/Data_FinalProject.csv")
X = df[df.columns[:-1]]
y = df["y"]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, stratify=y, test_size=0.25)
automl = AutoML(
# results_path="AutoML_22",
total_time_limit=30 * 60,
start_random_models=10,
hill_climbing_steps=3,
top_models_to_improve=3,
train_ensemble=True,
)
automl.fit(X_train, y_train)
pred = automl.predict(X_test)
print("Test accuracy", accuracy_score(y_test, pred))
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/regression_acs_fairness.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.automl import AutoML
# to get data
# from fairlearn.datasets import fetch_acs_income
# df = fetch_acs_income(as_frame=True)
# df["frame"].to_csv("acs_income.csv", index=False)
df = pd.read_csv("tests/data/acs_income_1k.csv")
print(df)
x_cols = [c for c in df.columns if c != "PINCP"]
sensitive_features = df["SEX"].astype(str)
X = df[x_cols]
y = df["PINCP"]
automl = AutoML(
algorithms=["Xgboost", "LightGBM"],
train_ensemble=True,
fairness_threshold=0.91,
# underprivileged_groups=[{"SEX": "1.0"}],
# privileged_groups=[{"SEX": "2.0"}]
)
automl.fit(X, y, sensitive_features=sensitive_features)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/multi_class_classifier_digits.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import pandas as pd
# scikit learn utilites
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# mljar-supervised package
from supervised.automl import AutoML
# Load the data
digits = load_digits()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
pd.DataFrame(digits.data), digits.target, stratify=digits.target, test_size=0.25
)
# train models
automl = AutoML(mode="Perform")
automl.fit(X_train, y_train)
# compute the accuracy on test data
predictions = automl.predict(X_test)
print(predictions.head())
print("Test accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, predictions["label"].astype(int)))
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/binary_classifier_random.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.automl import AutoML
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
import os
nrows = 100
ncols = 3
X = np.random.rand(nrows, ncols)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f{i}" for i in range(ncols)])
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, nrows)
# y = np.random.permutation(["a", "B"] * 50)
automl = AutoML(model_time_limit=10) # , algorithms=["Decision Tree"])
automl.fit(X, y)
print("Train accuracy", accuracy_score(y, automl.predict_all(X)["label"]))
# X = np.random.rand(1000, 10)
# X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f{i}" for i in range(10)])
# y = np.random.randint(0, 2, 1000)
# print("Test accuracy", accuracy_score(y, automl.predict(X)["label"]))
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/fairness/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
def accuracy(t, y):
return np.round(np.sum(t == y) / t.shape[0], 4)
def selection_rate(y):
return np.round(
np.sum((y == 1)) / y.shape[0],
4,
)
def true_positive_rate(t, y):
return np.round(
np.sum((y == 1) & (t == 1)) / np.sum((t == 1)),
4,
)
def false_positive_rate(t, y):
return np.round(
np.sum((y == 1) & (t == 0)) / np.sum((t == 0)),
4,
)
def true_negative_rate(t, y):
return np.round(
np.sum((y == 0) & (t == 0)) / np.sum((t == 0)),
4,
)
def false_negative_rate(t, y):
return np.round(
np.sum((y == 0) & (t == 1)) / np.sum((t == 1)),
4,
)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_utils/test_learning_curves.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import os
import unittest
from supervised.utils.learning_curves import LearningCurves
class LearningCurvesTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_plot_close(self):
"""
Test if we close plots. To avoid following warning:
RuntimeWarning: More than 20 figures have been opened.
Figures created through the pyplot interface (`matplotlib.pyplot.figure`)
are retained until explicitly closed and may consume too much memory.
"""
for _ in range(
1
): # you can increase the range, for tests speed reason I keep it low
LearningCurves.plot_for_ensemble([3, 2, 1], "random_metrics", ".")
os.remove(LearningCurves.output_file_name)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_update_errors_report.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import os
import shutil
import unittest
import numpy as np
from supervised import AutoML
class AutoMLUpdateErrorsReportTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "automl_testing"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_custom_init(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(30, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(30,))
automl = AutoML(results_path=self.automl_dir)
automl._update_errors_report("model_1", "bad error")
errors_filename = os.path.join(self.automl_dir, "errors.md")
self.assertTrue(os.path.exists(errors_filename))
with open(errors_filename) as file:
self.assertTrue("bad error" in file.read())
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/binary_classifier_adult_fairness.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
from supervised.automl import AutoML
data = fetch_openml(data_id=1590, as_frame=True)
X = data.data
# data.target #
y = data.target # (data.target == ">50K") * 1
sensitive_features = X[["sex"]]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, S_train, S_test = train_test_split(
X, y, sensitive_features, stratify=y, test_size=0.75, random_state=42
)
automl = AutoML(
algorithms=[
"Xgboost"
],
train_ensemble=False,
fairness_metric="demographic_parity_ratio",
fairness_threshold=0.8,
privileged_groups = [{"sex": "Male"}],
underprivileged_groups = [{"sex": "Female"}],
)
automl.fit(X_train, y_train, sensitive_features=S_train)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_utils/test_subsample.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.algorithms.registry import REGRESSION
from supervised.utils.subsample import subsample
class SubsampleTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_subsample_regression_10k(self):
rows = 10000
cols = 51
X = np.random.rand(rows, cols)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f{i}" for i in range(cols)])
y = pd.Series(np.random.rand(rows), name="target")
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = subsample(
X, y, train_size=1000, ml_task=REGRESSION
)
self.assertTrue(X_train.shape[0], 1000)
self.assertTrue(X_test.shape[0], 9000)
self.assertTrue(y_train.shape[0], 1000)
self.assertTrue(y_test.shape[0], 9000)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/tabular_mar_2021.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import pandas as pd
from supervised import AutoML
train = pd.read_csv("~/Downloads/tabular-playground-series-mar-2021/train.csv")
test = pd.read_csv("~/Downloads/tabular-playground-series-mar-2021/test.csv")
X_train = train.drop(["id", "target"], axis=1)
y_train = train.target
X_test = test.drop(["id"], axis=1)
automl = AutoML(
mode="Optuna",
eval_metric="auc",
algorithms=["CatBoost"],
optuna_time_budget=1800, # tune each algorithm for 30 minutes
total_time_limit=48
* 3600, # total time limit, set large enough to have time to compute all steps
features_selection=False,
)
automl.fit(X_train, y_train)
preds = automl.predict_proba(X_test)
submission = pd.DataFrame({"id": test.id, "target": preds[:, 1]})
submission.to_csv("1_submission.csv", index=False)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/utils/jsonencoder.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import json
from datetime import date
import numpy as np
class MLJSONEncoder(json.JSONEncoder):
def default(self, o):
if isinstance(
o,
(
np.int_,
np.intc,
np.intp,
np.int8,
np.int16,
np.int32,
np.int64,
np.uint8,
np.uint16,
np.uint32,
np.uint64,
),
):
return int(o)
elif isinstance(o, (np.float_, np.float16, np.float32, np.float64)):
return float(o)
elif isinstance(o, np.ndarray):
return o.tolist()
elif isinstance(obj, date):
return obj.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
return super(MLJSONEncoder, self).default(o)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/multi_class_classifier_MNIST.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from supervised.automl import AutoML
from supervised.utils.config import mem
df = pd.read_csv("tests/data/MNIST/train.csv")
X = df[[f for f in df.columns if "pixel" in f]]
y = df["label"]
for _ in range(4):
X = pd.concat([X, X], axis=0)
y = pd.concat([y, y], axis=0)
mem()
automl = AutoML(
# results_path="AutoML_12",
total_time_limit=60 * 60,
start_random_models=5,
hill_climbing_steps=2,
top_models_to_improve=3,
train_ensemble=True,
)
mem()
print("Start fit")
automl.fit(X, y)
test = pd.read_csv("tests/data/MNIST/test.csv")
predictions = automl.predict(test)
print(predictions.head())
print(predictions.tail())
sub = pd.DataFrame({"ImageId": 0, "Label": predictions["label"]})
sub["ImageId"] = sub.index + 1
sub.to_csv("sub1.csv", index=False)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/preprocessing/encoding_selector.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.preprocessing.preprocessing_categorical import PreprocessingCategorical
class EncodingSelector:
"""
EncodingSelector object decides which method should be used for categorical encoding.
Please keep it fast and simple. Thank you.
"""
@staticmethod
def get(X, y, column):
try:
unique_cnt = len(np.unique(X.loc[~pd.isnull(X[column]), column]))
if unique_cnt <= 20:
return PreprocessingCategorical.FEW_CATEGORIES
except Exception as e:
pass
return PreprocessingCategorical.MANY_CATEGORIES
"""
if unique_cnt <= 2 or unique_cnt > 25:
return PreprocessingCategorical.CONVERT_INTEGER
return PreprocessingCategorical.CONVERT_ONE_HOT
"""
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/test-installation-with-pip-on-windows.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```yaml
name: Test installation with pip on Windows
on:
schedule:
- cron: '0 8 * * 1'
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
build:
name: Run (${{ matrix.python-version }}, ${{ matrix.os }})
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
fail-fast: false
matrix:
os: [windows-latest]
python-version: ['3.9']
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
with:
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
- name: Check Python version
run: python --version
- name: Upgrade pip
run: python -m pip install --upgrade pip
- name: Install MLJAR AutoML
run: pip install mljar-supervised
- name: Try to import
run: python -c "import supervised; print(supervised.__version__)"
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_utils/test_shap.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.utils.shap import PlotSHAP
class PlotSHAPTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_get_sample_data_larger_1k(self):
"""Get sample when data is larger than 1k"""
X = pd.DataFrame(np.random.uniform(size=(5763, 31)))
y = pd.Series(np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(5763,)))
X_, y_ = PlotSHAP.get_sample(X, y)
self.assertEqual(X_.shape[0], 1000)
self.assertEqual(y_.shape[0], 1000)
def test_get_sample_data_smaller_1k(self):
"""Get sample when data is smaller than 1k"""
SAMPLES = 100
X = pd.DataFrame(np.random.uniform(size=(SAMPLES, 31)))
y = pd.Series(np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(SAMPLES,)))
X_, y_ = PlotSHAP.get_sample(X, y)
self.assertEqual(X_.shape[0], SAMPLES)
self.assertEqual(y_.shape[0], SAMPLES)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/test-installation-with-conda.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```yaml
name: Test installation with conda
on:
schedule:
- cron: '0 8 * * 1'
# run workflow manually
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
build:
name: Run (${{ matrix.python-version }}, ${{ matrix.os }})
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
fail-fast: false
matrix:
os: [windows-latest]
python-version: ['3.9']
steps:
- uses: conda-incubator/setup-miniconda@v2
with:
activate-environment: test
auto-update-conda: false
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
- name: Activate conda and check versions
run: |
conda activate test
conda --version
python --version
- name: Install MLJAR AutoML
run: conda install -c conda-forge mljar-supervised
- name: Try to import
run: python -c "import supervised;print(supervised.__version__)"
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/algorithms/factory.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
from supervised.algorithms.registry import BINARY_CLASSIFICATION, AlgorithmsRegistry
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
from supervised.exceptions import AutoMLException
class AlgorithmFactory(object):
@classmethod
def get_algorithm(cls, params):
alg_type = params.get("model_type", "Xgboost")
ml_task = params.get("ml_task", BINARY_CLASSIFICATION)
try:
Algorithm = AlgorithmsRegistry.get_algorithm_class(ml_task, alg_type)
return Algorithm(params)
except Exception as e:
raise AutoMLException(f"Cannot get algorithm class. {str(e)}")
@classmethod
def load(cls, json_desc, learner_path, lazy_load):
learner = AlgorithmFactory.get_algorithm(json_desc.get("params"))
learner.set_params(json_desc, learner_path)
if not lazy_load:
learner.reload()
return learner
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/callbacks/terminate_on_nan.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
import numpy as np
from supervised.callbacks.callback import Callback
class TerminateOnNan(Callback):
def __init__(self, learner, params):
super(TerminateOnNan, self).__init__(learner, params)
self.metric = Metric(params.get("metric_name"))
def on_iteration_end(self, iter_cnt, data):
loss_train = 0
if data.get("y_train_predicted") is not None:
loss_train = self.metric(
data.get("y_train_true"), data.get("y_train_predicted")
)
loss_validation = self.metric(
data.get("y_validation_true"), data.get("y_validation_predicted")
)
for loss in [loss_train, loss_validation]:
if np.isnan(loss) or np.isinf(loss) or np.isneginf(loss):
self.learner.stop_training = True
log.info("Terminating learning, invalid loss value")
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/binary_classifier.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.automl import AutoML
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import os
from sklearn.metrics import log_loss
import warnings
# warnings.filterwarnings("error", category=RuntimeWarning) #pd.core.common.SettingWithCopyWarning)
df = pd.read_csv(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pplonski/datasets-for-start/master/adult/data.csv",
skipinitialspace=True,
)
X = df[df.columns[:-1]]
y = df["income"]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
automl = AutoML(
algorithms=["LightGBM"],
mode="Compete",
explain_level=0,
train_ensemble=True,
golden_features=False,
features_selection=False,
eval_metric="auc",
)
automl.fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = automl.predict_all(X_test)
print(predictions.head())
print(predictions.tail())
print(X_test.shape, predictions.shape)
print("LogLoss", log_loss(y_test, predictions["prediction_>50K"]))
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_adjust_validation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import os
import shutil
import unittest
import numpy as np
from supervised import AutoML
class AutoMLAdjustValidationTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "automl_testing"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_custom_init(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(60, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(60,))
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
model_time_limit=10,
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
mode="Compete",
explain_level=0,
start_random_models=1,
hill_climbing_steps=0,
top_models_to_improve=0,
kmeans_features=False,
golden_features=False,
features_selection=False,
boost_on_errors=False,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
self.assertFalse(
os.path.exists(os.path.join(self.automl_dir, "1_DecisionTree"))
)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/multi_class_drug_fairness.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from supervised import AutoML
df = pd.read_csv("tests/data/Drug/Drug_Consumption.csv")
X = df[df.columns[1:13]]
# convert to 3 classes
df = df.replace(
{
"Cannabis": {
"CL0": "never_used",
"CL1": "not_in_last_year",
"CL2": "not_in_last_year",
"CL3": "used_in_last_year",
"CL4": "used_in_last_year",
"CL5": "used_in_last_year",
"CL6": "used_in_last_year",
}
}
)
y = df["Cannabis"]
# maybe should be
# The binary sensitive feature is education level (college degree or not).
# like in
# Fairness guarantee in multi-class classification
sensitive_features = df["Gender"]
automl = AutoML(
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
train_ensemble=True,
start_random_models=3,
hill_climbing_steps=3,
top_models_to_improve=2,
fairness_threshold=0.8,
explain_level=1
)
automl.fit(X, y, sensitive_features=sensitive_features)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_preprocessing/test_datetime_transformer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import pandas as pd
from supervised.preprocessing.datetime_transformer import DateTimeTransformer
class DateTimeTransformerTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_transformer(self):
d = {
"col1": [
"2020/06/01",
"2020/06/02",
"2020/06/03",
"2021/06/01",
"2022/06/01",
]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
df["col1"] = pd.to_datetime(df["col1"])
df_org = df.copy()
transf = DateTimeTransformer()
transf.fit(df, "col1")
df = transf.transform(df)
self.assertTrue(df.shape[0] == 5)
self.assertTrue("col1" not in df.columns)
self.assertTrue("col1_Year" in df.columns)
transf2 = DateTimeTransformer()
transf2.from_json(transf.to_json())
df2 = transf2.transform(df_org)
self.assertTrue("col1" not in df2.columns)
self.assertTrue("col1_Year" in df2.columns)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_preprocessing/test_text_transformer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import pandas as pd
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from supervised.preprocessing.text_transformer import TextTransformer
class TextTransformerTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_transformer(self):
d = {
"col1": [
"This is the first document.",
"This document is the second document.",
"And this is the third one.",
None,
"Is this the first document?",
]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
df_org = df.copy()
transf = TextTransformer()
transf.fit(df, "col1")
df = transf.transform(df)
self.assertTrue(df.shape[0] == 5)
self.assertTrue("col1" not in df.columns)
transf2 = TextTransformer()
transf2.from_json(transf.to_json())
df2 = transf2.transform(df_org)
self.assertTrue("col1" not in df2.columns)
assert_almost_equal(df.iloc[0, 0], df2.iloc[0, 0])
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_utils/test_importance.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import os
import tempfile
import unittest
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from supervised.utils.importance import PermutationImportance
class PermutationImportanceTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_compute_and_plot(self):
rows = 20
X = np.random.rand(rows, 3)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f{i}" for i in range(3)])
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, rows)
model = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1)
model.fit(X, y)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdir:
PermutationImportance.compute_and_plot(
model,
X_validation=X,
y_validation=y,
model_file_path=tmpdir,
learner_name="learner_test",
metric_name=None,
ml_task="binary_classification",
)
self.assertTrue(
os.path.exists(os.path.join(tmpdir, "learner_test_importance.csv"))
)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/callbacks/callback_list.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
class CallbackList(object):
def __init__(self, callbacks=[]):
self.callbacks = callbacks
def add_and_set_learner(self, learner):
for cb in self.callbacks:
cb.add_and_set_learner(learner)
def on_learner_train_start(self, logs=None):
for cb in self.callbacks:
cb.on_learner_train_start(logs)
def on_learner_train_end(self, logs=None):
for cb in self.callbacks:
cb.on_learner_train_end(logs)
def on_iteration_start(self, logs=None):
for cb in self.callbacks:
cb.on_iteration_start(logs)
def on_iteration_end(self, logs=None, predictions=None):
for cb in self.callbacks:
cb.on_iteration_end(logs, predictions)
def on_framework_train_end(self, logs=None):
for cb in self.callbacks:
cb.on_framework_train_end(logs)
def get(self, callback_name):
for cb in self.callbacks:
if cb.name == callback_name:
return cb
return None
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/utils/common.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import os
def construct_learner_name(fold, repeat, repeats):
repeat_str = f"_repeat_{repeat}" if repeats > 1 else ""
return f"learner_fold_{fold}{repeat_str}"
def learner_name_to_fold_repeat(name):
fold, repeat = None, None
arr = name.split("_")
fold = int(arr[2])
if "repeat" in name:
repeat = int(arr[4])
return fold, repeat
def get_fold_repeat_cnt(model_path):
training_logs = [f for f in os.listdir(model_path) if "_training.log" in f]
fold_cnt, repeat_cnt = 0, 0
for fname in training_logs:
fold, repeat = learner_name_to_fold_repeat(fname)
if fold is not None:
fold_cnt = max(fold_cnt, fold)
if repeat is not None:
repeat_cnt = max(repeat_cnt, repeat)
fold_cnt += 1 # counting from 0
repeat_cnt += 1
return fold_cnt, repeat_cnt
def get_learners_names(model_path):
postfix = "_training.log"
learner_names = [
f.repleace(postfix, "") for f in os.listdir(model_path) if postfix in f
]
return learner_names
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_ensemble/test_save_load.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import shutil
import unittest
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import datasets
from supervised import AutoML
class EnsembleSaveLoadTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "EnsembleSaveLoadTest"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_save_load(self):
a = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=10,
explain_level=0,
mode="Explain",
train_ensemble=True,
start_random_models=1,
)
X, y = datasets.make_classification(
n_samples=100,
n_features=5,
n_informative=4,
n_redundant=1,
n_classes=2,
n_clusters_per_class=3,
n_repeated=0,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f_{i}" for i in range(X.shape[1])])
a.fit(X, y)
p = a.predict(X)
a2 = AutoML(results_path=self.automl_dir)
p2 = a2.predict(X)
self.assertTrue((p == p2).all())
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/validation/validation_step.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
from supervised.exceptions import AutoMLException
from supervised.validation.validator_custom import CustomValidator
from supervised.validation.validator_kfold import KFoldValidator
from supervised.validation.validator_split import SplitValidator
class ValidationStep:
def __init__(self, params):
# kfold is default validation technique
self.validation_type = params.get("validation_type", "kfold")
if self.validation_type == "kfold":
self.validator = KFoldValidator(params)
elif self.validation_type == "split":
self.validator = SplitValidator(params)
elif self.validation_type == "custom":
self.validator = CustomValidator(params)
else:
raise AutoMLException(
f"The validation type ({self.validation_type}) is not implemented."
)
def get_split(self, k, repeat=0):
return self.validator.get_split(k, repeat)
def split(self):
return self.validator.split()
def get_n_splits(self):
return self.validator.get_n_splits()
def get_repeats(self):
return self.validator.get_repeats()
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_automl_report.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import os
import shutil
import unittest
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import pytest
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from supervised import AutoML
from supervised.exceptions import AutoMLException
iris = datasets.load_iris()
class AutoMLReportTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "AutoMLTest"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def setUp(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_report(self):
"""Tests AutoML in the iris dataset (Multiclass classification)"""
model = AutoML(
algorithms=["Baseline"],
explain_level=0, verbose=0, random_state=1, results_path=self.automl_dir
)
model.fit(iris.data, iris.target)
model.report()
report_path = os.path.join(self.automl_dir, "README.html")
self.assertTrue(os.path.exists(report_path))
content = None
with open(report_path, "r") as fin:
content = fin.read()
#print(content)
link = '<a href="1_Baseline/README.html">'
self.assertFalse(link in content)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/checks/check_automl_with_regression.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import pandas as pd
import sklearn.model_selection
from supervised.automl import AutoML
class AutoMLWithRegressionTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_fit_and_predict(self):
seed = 1709
df = pd.read_csv(
"./tests/data/housing_regression_missing_values_missing_target.csv"
)
print(df.columns)
x_cols = [c for c in df.columns if c != "MEDV"]
X = df[x_cols]
y = df["MEDV"]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=seed
)
automl = AutoML(
total_time_limit=10,
algorithms=["Xgboost"], # ["LightGBM", "RF", "NN", "CatBoost", "Xgboost"],
start_random_models=1,
hill_climbing_steps=0,
top_models_to_improve=0,
train_ensemble=True,
verbose=True,
)
automl.fit(X_train, y_train)
response = automl.predict(X_test) # ["p_1"]
print("Response", response)
# Compute the logloss on test dataset
# ll = log_loss(y_test, response)
# print("(*) Dataset id {} logloss {}".format(dataset_id, ll))
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_data_types.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import shutil
import unittest
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised import AutoML
class AutoMLDataTypesTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "automl_tests"
rows = 250
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_category_data_type(self):
X = np.random.rand(self.rows, 3)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f{i}" for i in range(3)])
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, self.rows)
X["f1"] = X["f1"].astype("category")
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=1,
algorithms=["CatBoost"],
train_ensemble=False,
explain_level=0,
start_random_models=1,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
def test_encoding_strange_characters(self):
X = np.random.rand(self.rows, 3)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f{i}" for i in range(3)])
y = np.random.permutation(["ɛ", "🂲"] * int(self.rows / 2))
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=1,
algorithms=["Baseline"],
train_ensemble=False,
explain_level=0,
start_random_models=1,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/run-tests.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```yaml
name: Tests
on: [ push,pull_request ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
matrix:
os: [ ubuntu-latest ]
python-version: [ '3.10']
#os: [ ubuntu-latest, macos-latest, windows-latest ]
#python-version: [ '3.8', '3.9', '3.10', '3.11' ]
steps:
- name: Install OS Dependencies
if: matrix.os == 'ubuntu-latest'
run: |
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get -y install graphviz
- name: Install OS Dependencies
if: matrix.os == 'macos-latest'
run: |
brew install graphviz
- name: Install OS Dependencies
if: matrix.os == 'windows-latest'
run: |
choco install graphviz
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
uses: actions/setup-python@v2
with:
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
- name: Install Python Dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install --upgrade setuptools
pip install -U importlib-metadata>=1.7.0
pip install -U -r requirements.txt
pip install -U -r requirements_dev.txt
pip install ipython
python setup.py install
- name: Test with pytest
run: |
pytest tests --cov=supervised/
continue-on-error: true
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/utils/data_validation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
def check_greater_than_zero_integer(value, original_var_name):
if not isinstance(value, int):
raise ValueError(
f"'{original_var_name}' must be an integer, got '{type(value)}'."
)
if value <= 0:
raise ValueError(
f"'{original_var_name}' must be greater than zero, got '{value}'."
)
def check_positive_integer(value, original_var_name):
if not isinstance(value, int):
raise ValueError(
f"'{original_var_name}' must be an integer, got '{type(value)}'."
)
if value < 0:
raise ValueError(
f"'{original_var_name}' must be equal or greater than zero, got '{value}'."
)
def check_integer(value, original_var_name):
if not isinstance(value, int):
raise ValueError(
f"'{original_var_name}' must be an integer, got '{type(value)}'."
)
def check_bool(value, original_var_name):
if not isinstance(value, bool):
raise ValueError(
f"'{original_var_name}' must be a boolean, got '{type(value)}'."
)
def check_greater_than_zero_integer_or_float(value, original_var_name):
if not (isinstance(value, int) or isinstance(value, float)):
raise ValueError(
f"'{original_var_name}' must be an integer or float, got '{type(value)}'."
)
if value <= 0:
raise ValueError(
f"'{original_var_name}' must be greater than zero, got '{value}'."
)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
from setuptools import setup, find_packages
from codecs import open
from os import path
here = path.abspath(path.dirname(__file__))
# Get the long description from the README file
with open(path.join(here, "README.md"), encoding="utf-8") as f:
long_description = f.read()
setup(
name="mljar-supervised",
version="1.1.18",
description="Automated Machine Learning for Humans",
long_description=long_description,
long_description_content_type="text/markdown",
url="https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised",
author="MLJAR, Sp. z o.o.",
author_email="[email protected]",
license="MIT",
packages=find_packages(exclude=["*.tests", "*.tests.*", "tests.*", "tests"]),
install_requires=open("requirements.txt").readlines(),
include_package_data=True,
python_requires='>=3.8',
classifiers=[
"Programming Language :: Python",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.8",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.9",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.10",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.11",
],
keywords=[
"automated machine learning",
"automl",
"machine learning",
"data science",
"data mining",
"mljar",
"random forest",
"decision tree",
"xgboost",
"lightgbm",
"catboost",
"neural network",
"extra trees",
"linear model",
"features selection",
"features engineering"
],
)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/preprocessing/exclude_missing_target.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
import warnings
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.utils.config import LOG_LEVEL
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.setLevel(LOG_LEVEL)
class ExcludeRowsMissingTarget(object):
@staticmethod
def transform(
X=None, y=None, sample_weight=None, sensitive_features=None, warn=False
):
if y is None:
return X, y, sample_weight, sensitive_features
y_missing = pd.isnull(y)
if np.sum(np.array(y_missing)) == 0:
return X, y, sample_weight, sensitive_features
logger.debug("Exclude rows with missing target values")
if warn:
warnings.warn(
"There are samples with missing target values in the data which will be excluded for further analysis",
UserWarning
)
y = y.drop(y.index[y_missing])
y.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)
if X is not None:
X = X.drop(X.index[y_missing])
X.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)
if sample_weight is not None:
sample_weight = sample_weight.drop(sample_weight.index[y_missing])
sample_weight.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)
if sensitive_features is not None:
sensitive_features = sensitive_features.drop(
sensitive_features.index[y_missing]
)
sensitive_features.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)
return X, y, sample_weight, sensitive_features
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_prediction_after_load.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import shutil
import unittest
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from supervised import AutoML
class AutoMLPredictionAfterLoadTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "AutoMLPredictionAfterLoadTest"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_integration(self):
a = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
mode="Compete",
algorithms=["Baseline", "CatBoost", "LightGBM", "Xgboost"],
stack_models=True,
total_time_limit=60,
validation_strategy={
"validation_type": "kfold",
"k_folds": 3,
"shuffle": True,
"stratify": True,
"random_seed": 123,
},
)
X, y = datasets.make_classification(
n_samples=1000,
n_features=30,
n_informative=29,
n_redundant=1,
n_classes=8,
n_clusters_per_class=3,
n_repeated=0,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, train_size=0.8)
a.fit(X_train, y_train)
p = a.predict_all(X_test)
a2 = AutoML(results_path=self.automl_dir)
p2 = a2.predict_all(X_test)
assert_almost_equal(p["prediction_0"].iloc[0], p2["prediction_0"].iloc[0])
assert_almost_equal(p["prediction_7"].iloc[0], p2["prediction_7"].iloc[0])
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/binary_classifier_ensemble.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import pandas as pd
from supervised.automl import AutoML
from supervised.ensemble import Ensemble
import os
df = pd.read_csv(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pplonski/datasets-for-start/master/adult/data.csv",
skipinitialspace=True,
)
X = df[df.columns[:-1]]
y = df["income"]
results_path = "AutoML_2"
automl = AutoML(
results_path=results_path,
total_time_limit=400,
start_random_models=10,
hill_climbing_steps=0,
top_models_to_improve=0,
train_ensemble=False,
)
models_map = {m.get_name(): m for m in automl._models}
ensemble = Ensemble("logloss", "binary_classification")
ensemble.models_map = models_map
oofs = {}
target = None
for i in range(1, 30):
oof = pd.read_csv(
os.path.join(results_path, f"model_{i}", "predictions_out_of_folds.csv")
)
prediction_cols = [c for c in oof.columns if "prediction" in c]
oofs[f"model_{i}"] = oof[prediction_cols]
if target is None:
target_columns = [c for c in oof.columns if "target" in c]
target = oof[target_columns]
ensemble.target = target
ensemble.target_columns = "target"
ensemble.fit(oofs, target)
ensemble.save(os.path.join(results_path, "ensemble"))
predictions = ensemble.predict(X)
print(predictions.head())
"""
p_<=50K p_>50K
0 0.982940 0.017060
1 0.722781 0.277219
2 0.972687 0.027313
3 0.903021 0.096979
4 0.591373 0.408627
"""
ensemble2 = Ensemble.load(os.path.join(results_path, "ensemble"), models_map)
predictions2 = ensemble2.predict(X)
print(predictions2.head())
"""
p_<=50K p_>50K
0 0.982940 0.017060
1 0.722781 0.277219
2 0.972687 0.027313
3 0.903021 0.096979
4 0.591373 0.408627
"""
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/callbacks/learner_time_constraint.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
import time
import numpy as np
from supervised.callbacks.callback import Callback
from supervised.utils.config import LOG_LEVEL
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
log.setLevel(LOG_LEVEL)
class LearnerTimeConstraint(Callback):
def __init__(self, params={}):
super(LearnerTimeConstraint, self).__init__(params)
self.name = params.get("name", "learner_time_constraint")
self.min_steps = params.get("min_steps")
self.learner_time_limit = params.get("learner_time_limit") # in seconds
self.iterations_count = 0
def on_learner_train_start(self, logs):
self.train_start_time = time.time()
self.iterations_count = 0
def on_iteration_start(self, logs):
self.iter_start_time = time.time()
def on_iteration_end(self, logs, predictions):
self.iterations_count += 1
iteration_elapsed_time = np.round(time.time() - self.iter_start_time, 2)
learner_elapsed_time = np.round(time.time() - self.train_start_time, 2)
log.debug(
"Iteration {0} took {1} seconds, learner training time {2} seconds".format(
self.iterations_count, iteration_elapsed_time, learner_elapsed_time
)
)
if self.min_steps is not None:
if self.iterations_count < self.min_steps:
# self.learner.stop_training = False
# return before checking other conditions
return
if self.learner_time_limit is not None:
if learner_elapsed_time >= self.learner_time_limit:
self.learner.stop_training = True
log.info("Terminating learning, time limit reached")
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_restore.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import json
import os
import shutil
import unittest
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised import AutoML
from supervised.algorithms.xgboost import additional
additional["max_rounds"] = 1
class AutoMLRestoreTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "automl_tests"
rows = 50
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_tune_only_default(self):
X = np.random.rand(self.rows, 3)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f{i}" for i in range(3)])
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, self.rows)
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=3,
algorithms=["Decision Tree"],
explain_level=0,
train_ensemble=False,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
# Get number of starting models
n1 = len([x for x in os.listdir(self.automl_dir) if x[0].isdigit()])
with open(os.path.join(self.automl_dir, "progress.json"), "r") as file:
progress = json.load(file)
progress["fit_level"] = "default_algorithms"
with open(os.path.join(self.automl_dir, "progress.json"), "w") as fout:
fout.write(json.dumps(progress, indent=4))
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=3,
algorithms=["Decision Tree", "Xgboost"],
explain_level=0,
train_ensemble=False,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
# Get number of models after second fit
n2 = len([x for x in os.listdir(self.automl_dir) if x[0].isdigit()])
# number of models should be equal
# user cannot overwrite parameters
self.assertEqual(n2, n1)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/preprocessing/label_encoder.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
from decimal import Decimal
import numpy as np
from sklearn import preprocessing as sk_preproc
from supervised.utils.config import LOG_LEVEL
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.setLevel(LOG_LEVEL)
class LabelEncoder(object):
def __init__(self, try_to_fit_numeric=False):
self.lbl = sk_preproc.LabelEncoder()
self._try_to_fit_numeric = try_to_fit_numeric
def fit(self, x):
self.lbl.fit(x) # list(x.values))
if self._try_to_fit_numeric:
logger.debug("Try to fit numeric in LabelEncoder")
try:
arr = {Decimal(c): c for c in self.lbl.classes_}
sorted_arr = dict(sorted(arr.items()))
self.lbl.classes_ = np.array(
list(sorted_arr.values()), dtype=self.lbl.classes_.dtype
)
except Exception as e:
pass
def transform(self, x):
try:
return self.lbl.transform(x) # list(x.values))
except ValueError as ve:
# rescue
classes = np.unique(x) # list(x.values))
diff = np.setdiff1d(classes, self.lbl.classes_)
self.lbl.classes_ = np.concatenate((self.lbl.classes_, diff))
return self.lbl.transform(x) # list(x.values))
def inverse_transform(self, x):
return self.lbl.inverse_transform(x) # (list(x.values))
def to_json(self):
data_json = {}
for i, cl in enumerate(self.lbl.classes_):
data_json[str(cl)] = i
return data_json
def from_json(self, data_json):
keys = np.array(list(data_json.keys()))
if len(keys) == 2 and "False" in keys and "True" in keys:
keys = np.array([False, True])
self.lbl.classes_ = keys
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_preprocessing/test_exclude_missing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.preprocessing.exclude_missing_target import ExcludeRowsMissingTarget
class ExcludeRowsMissingTargetTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_transform(self):
d_test = {
"col1": [1, 1, np.nan, 3],
"col2": ["a", "a", np.nan, "a"],
"col3": [1, 1, 1, 3],
"col4": ["a", "a", "b", "c"],
"y": [np.nan, 1, np.nan, 2],
}
df_test = pd.DataFrame(data=d_test)
X = df_test.loc[:, ["col1", "col2", "col3", "col4"]]
y = df_test.loc[:, "y"]
self.assertEqual(X.shape[0], 4)
self.assertEqual(y.shape[0], 4)
X, y, _, _ = ExcludeRowsMissingTarget.transform(X, y)
self.assertEqual(X.shape[0], 2)
self.assertEqual(y.shape[0], 2)
self.assertEqual(y[0], 1)
self.assertEqual(y[1], 2)
def test_transform_with_sample_weight(self):
d_test = {
"col1": [1, 1, np.nan, 3],
"col2": ["a", "a", np.nan, "a"],
"col3": [1, 1, 1, 3],
"col4": ["a", "a", "b", "c"],
"sample_weight": [1, 2, 3, 4],
"y": [np.nan, 1, np.nan, 2],
}
df_test = pd.DataFrame(data=d_test)
X = df_test.loc[:, ["col1", "col2", "col3", "col4"]]
y = df_test.loc[:, "y"]
sample_weight = df_test.loc[:, "sample_weight"]
self.assertEqual(X.shape[0], 4)
self.assertEqual(y.shape[0], 4)
X, y, sw, _ = ExcludeRowsMissingTarget.transform(X, y, sample_weight)
self.assertEqual(X.shape[0], 2)
self.assertEqual(y.shape[0], 2)
self.assertEqual(sw.shape[0], 2)
self.assertEqual(y[0], 1)
self.assertEqual(y[1], 2)
self.assertEqual(sw[0], 2)
self.assertEqual(sw[1], 4)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_fairness/test_multi_class_classification.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import shutil
import unittest
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised import AutoML
class FairnessInMultiClassClassificationTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "automl_fairness_testing"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_init(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(30, 2))
y = np.array(["A", "B", "C"] * 10)
S = pd.DataFrame({"sensitive": ["D", "E"] * 15})
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
model_time_limit=10,
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
explain_level=0,
train_ensemble=False,
stack_models=False,
validation_strategy={"validation_type": "split"},
start_random_models=1,
)
automl.fit(X, y, sensitive_features=S)
self.assertGreater(len(automl._models), 0)
sensitive_features_names = automl._models[0].get_sensitive_features_names()
self.assertEqual(len(sensitive_features_names), 3)
self.assertTrue("sensitive__A" in sensitive_features_names)
self.assertTrue("sensitive__B" in sensitive_features_names)
self.assertTrue("sensitive__C" in sensitive_features_names)
self.assertTrue(
automl._models[0].get_fairness_metric("sensitive__A") is not None
)
self.assertTrue(
automl._models[0].get_fairness_metric("sensitive__B") is not None
)
self.assertTrue(
automl._models[0].get_fairness_metric("sensitive__C") is not None
)
self.assertTrue(len(automl._models[0].get_fairness_optimization()) > 1)
self.assertTrue(automl._models[0].get_worst_fairness() is not None)
self.assertTrue(automl._models[0].get_best_fairness() is not None)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/callbacks/metric_logger.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
from supervised.callbacks.callback import Callback
from supervised.utils.metric import Metric
class MetricLogger(Callback):
def __init__(self, params):
super(MetricLogger, self).__init__(params)
self.name = params.get("name", "metric_logger")
self.loss_values = {}
self.metrics = []
for metric_name in params.get("metric_names"):
self.metrics += [Metric({"name": metric_name})]
def add_and_set_learner(self, learner):
self.loss_values[learner.uid] = {"train": {}, "validation": {}, "iters": []}
for metric in self.metrics:
self.loss_values[learner.uid]["train"][metric.name] = []
self.loss_values[learner.uid]["validation"][metric.name] = []
self.current_learner_uid = learner.uid
def on_iteration_end(self, logs, predictions):
for metric in self.metrics:
train_loss = 0
if predictions.get("y_train_predicted") is not None:
train_loss = metric(
predictions.get("y_train_true"),
predictions.get("y_train_predicted"),
)
validation_loss = metric(
predictions.get("y_validation_true"),
predictions.get("y_validation_predicted"),
)
self.loss_values[self.current_learner_uid]["train"][metric.name] += [
train_loss
]
self.loss_values[self.current_learner_uid]["validation"][metric.name] += [
validation_loss
]
# keep information about iter number only once :)
if metric == self.metrics[0]:
self.loss_values[self.current_learner_uid]["iters"] += [
logs.get("iter_cnt")
]
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/tuner/optuna/knn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import optuna
from supervised.algorithms.knn import KNeighborsAlgorithm, KNeighborsRegressorAlgorithm
from supervised.algorithms.registry import (
REGRESSION,
)
from supervised.utils.metric import Metric
class KNNObjective:
def __init__(
self,
ml_task,
X_train,
y_train,
sample_weight,
X_validation,
y_validation,
sample_weight_validation,
eval_metric,
n_jobs,
random_state,
):
self.ml_task = ml_task
self.X_train = X_train
self.y_train = y_train
self.sample_weight = sample_weight
self.X_validation = X_validation
self.y_validation = y_validation
self.eval_metric = eval_metric
self.n_jobs = n_jobs
self.seed = random_state
def __call__(self, trial):
try:
params = {
"n_neighbors": trial.suggest_int("n_neighbors", 1, 128),
"weights": trial.suggest_categorical(
"weights", ["uniform", "distance"]
),
"n_jobs": self.n_jobs,
"rows_limit": 100000,
"ml_task": self.ml_task,
}
Algorithm = (
KNeighborsRegressorAlgorithm
if self.ml_task == REGRESSION
else KNeighborsAlgorithm
)
model = Algorithm(params)
model.fit(self.X_train, self.y_train, sample_weight=self.sample_weight)
preds = model.predict(self.X_validation)
score = self.eval_metric(self.y_validation, preds)
if Metric.optimize_negative(self.eval_metric.name):
score *= -1.0
except optuna.exceptions.TrialPruned as e:
raise e
except Exception as e:
print("Exception in KNNObjective", str(e))
return None
return score
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_automl_init.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import shutil
import unittest
import numpy as np
from supervised import AutoML
class AutoMLInitTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "AutoMLInitTest"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_custom_init(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(30, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(30,))
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
model_time_limit=1,
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
explain_level=0,
train_ensemble=False,
stack_models=False,
validation_strategy={"validation_type": "split"},
start_random_models=3,
hill_climbing_steps=1,
top_models_to_improve=1,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
self.assertGreater(len(automl._models), 3)
def test_get_results_path(self):
automl = AutoML(algorithms=["Baseline"], total_time_limit=1)
first_path = automl._get_results_path()
self.assertEqual(first_path, automl._get_results_path())
shutil.rmtree(first_path, ignore_errors=True)
automl = AutoML(
algorithms=["Baseline"], total_time_limit=1, results_path=self.automl_dir
)
self.assertEqual(self.automl_dir, automl._get_results_path())
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
# get results path after save
automl = AutoML(
algorithms=["Baseline"], total_time_limit=1, results_path=self.automl_dir
)
X = np.random.uniform(size=(30, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(30,))
automl.fit(X, y)
self.assertEqual(self.automl_dir, automl._get_results_path())
automl2 = AutoML(
algorithms=["Baseline"], total_time_limit=1, results_path=self.automl_dir
)
self.assertEqual(self.automl_dir, automl2._get_results_path())
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_stack_models_constraints.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import shutil
import unittest
import numpy as np
from supervised import AutoML
class AutoMLStackModelsConstraintsTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "AutoMLStackModelsConstraintsTest"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_allow_stack_models(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(100, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(100,))
X[:, 0] = y
X[:, 1] = -y
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=5,
mode="Compete",
validation_strategy={"validation_type": "kfold", "k_folds": 5},
)
automl.fit(X, y)
self.assertTrue(automl._stack_models)
self.assertTrue(automl.tuner._stack_models)
self.assertTrue(automl._time_ctrl._is_stacking)
def test_disable_stack_models(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(100, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(100,))
X[:, 0] = y
X[:, 1] = -y
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=5,
mode="Compete",
validation_strategy={"validation_type": "split"},
)
automl.fit(X, y)
self.assertFalse(automl._stack_models)
self.assertFalse(automl.tuner._stack_models)
self.assertFalse(automl._time_ctrl._is_stacking)
def test_disable_stack_models_adjusted_validation(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(100, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(100,))
X[:, 0] = y
X[:, 1] = -y
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir, total_time_limit=5, mode="Compete"
)
automl.fit(X, y)
# the stacking should be disabled
# because of small time limit
self.assertFalse(automl._stack_models)
self.assertFalse(automl.tuner._stack_models)
self.assertFalse(automl._time_ctrl._is_stacking)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_algorithms/test_decision_tree.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import os
import tempfile
import unittest
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from sklearn import datasets
from supervised.algorithms.decision_tree import (
DecisionTreeRegressorAlgorithm,
)
from supervised.utils.metric import Metric
class DecisionTreeTest(unittest.TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
cls.X, cls.y = datasets.make_regression(
n_samples=100,
n_features=5,
n_informative=4,
n_targets=1,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
def test_reproduce_fit_regression(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "rmse"})
params = {"max_depth": 1, "seed": 1, "ml_task": "regression"}
prev_loss = None
for _ in range(3):
model = DecisionTreeRegressorAlgorithm(params)
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = model.predict(self.X)
loss = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
if prev_loss is not None:
assert_almost_equal(prev_loss, loss)
prev_loss = loss
def test_save_and_load(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "rmse"})
dt = DecisionTreeRegressorAlgorithm({"ml_task": "regression"})
dt.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = dt.predict(self.X)
loss = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
filename = os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), os.urandom(12).hex())
dt.save(filename)
dt2 = DecisionTreeRegressorAlgorithm({"ml_task": "regression"})
dt2.load(filename)
y_predicted = dt2.predict(self.X)
loss2 = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
assert_almost_equal(loss, loss2)
# Finished with temp file, delete it
os.remove(filename)
def test_is_fitted(self):
params = {"max_depth": 1, "seed": 1, "ml_task": "regression"}
model = DecisionTreeRegressorAlgorithm(params)
self.assertFalse(model.is_fitted())
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
self.assertTrue(model.is_fitted())
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_callbacks/test_total_time_constraint.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import time
import unittest
from supervised.callbacks.total_time_constraint import TotalTimeConstraint
from supervised.exceptions import NotTrainedException
class TotalTimeConstraintTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_stop_on_first_learner(self):
params = {
"total_time_limit": 100,
"total_time_start": time.time(),
"expected_learners_cnt": 1001,
}
callback = TotalTimeConstraint(params)
callback.add_and_set_learner(learner={})
callback.on_learner_train_start(logs=None)
time.sleep(0.1)
with self.assertRaises(NotTrainedException) as context:
callback.on_learner_train_end(logs=None)
self.assertTrue("Stop training after the first fold" in str(context.exception))
def test_stop_on_not_first_learner(self):
params = {
"total_time_limit": 100,
"total_time_start": time.time(),
"expected_learners_cnt": 10,
}
callback = TotalTimeConstraint(params)
callback.add_and_set_learner(learner={})
callback.on_learner_train_start(logs=None)
callback.on_learner_train_end(logs=None)
with self.assertRaises(NotTrainedException) as context:
#
# hardcoded change just for tests!
callback.total_time_start = time.time() - 600 - 100 - 1
#
callback.add_and_set_learner(learner={})
callback.on_learner_train_start(logs=None)
callback.on_learner_train_end(logs=None)
self.assertTrue("Force to stop" in str(context.exception))
def test_dont_stop(self):
params = {
"total_time_limit": 100,
"total_time_start": time.time(),
"expected_learners_cnt": 10,
}
callback = TotalTimeConstraint(params)
for i in range(10):
callback.add_and_set_learner(learner={})
callback.on_learner_train_start(logs=None)
callback.on_learner_train_end(logs=None)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_preprocessing/test_preprocessing_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.preprocessing.preprocessing_utils import PreprocessingUtils
class PreprocessingUtilsTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_get_type_numpy_number(self):
tmp = np.array([1, 2, 3])
tmp_type = PreprocessingUtils.get_type(tmp)
self.assertNotEqual(tmp_type, PreprocessingUtils.CATEGORICAL)
def test_get_type_numpy_categorical(self):
tmp = np.array(["a", "b", "c"])
tmp_type = PreprocessingUtils.get_type(tmp)
self.assertEqual(tmp_type, PreprocessingUtils.CATEGORICAL)
def test_get_type_pandas_bug(self):
d = {"col1": [1, 2, 3], "col2": ["a", "b", "c"]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
col1_type = PreprocessingUtils.get_type(df.loc[:, "col2"])
self.assertEqual(col1_type, PreprocessingUtils.CATEGORICAL)
def test_get_type_pandas(self):
d = {"col1": [1, 2, 3], "col2": ["a", "b", "c"]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
col1_type = PreprocessingUtils.get_type(df["col1"])
self.assertNotEqual(col1_type, PreprocessingUtils.CATEGORICAL)
col2_type = PreprocessingUtils.get_type(df["col2"])
self.assertNotEqual(col1_type, PreprocessingUtils.CATEGORICAL)
def test_get_stats(self):
tmp = np.array([1, np.nan, 2, 3, np.nan, np.nan])
self.assertEqual(1, PreprocessingUtils.get_min(tmp))
self.assertEqual(2, PreprocessingUtils.get_mean(tmp))
self.assertEqual(2, PreprocessingUtils.get_median(tmp))
d = {"col1": [1, 2, 1, 3, 1, np.nan], "col2": ["a", np.nan, "b", "a", "c", "a"]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
self.assertEqual(1, PreprocessingUtils.get_min(df["col1"]))
self.assertEqual(8.0 / 5.0, PreprocessingUtils.get_mean(df["col1"]))
self.assertEqual(1, PreprocessingUtils.get_median(df["col1"]))
self.assertEqual(1, PreprocessingUtils.get_most_frequent(df["col1"]))
self.assertEqual("a", PreprocessingUtils.get_most_frequent(df["col2"]))
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/tuner/optuna/nn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import optuna
from supervised.algorithms.nn import MLPAlgorithm, MLPRegressorAlgorithm
from supervised.algorithms.registry import (
REGRESSION,
)
from supervised.utils.metric import Metric
class NeuralNetworkObjective:
def __init__(
self,
ml_task,
X_train,
y_train,
sample_weight,
X_validation,
y_validation,
sample_weight_validation,
eval_metric,
n_jobs,
random_state,
):
self.ml_task = ml_task
self.X_train = X_train
self.y_train = y_train
self.sample_weight = sample_weight
self.X_validation = X_validation
self.y_validation = y_validation
self.eval_metric = eval_metric
self.seed = random_state
def __call__(self, trial):
try:
Algorithm = (
MLPRegressorAlgorithm if self.ml_task == REGRESSION else MLPAlgorithm
)
params = {
"dense_1_size": trial.suggest_int("dense_1_size", 4, 100),
"dense_2_size": trial.suggest_int("dense_2_size", 2, 100),
"learning_rate": trial.suggest_categorical(
"learning_rate", [0.005, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2]
),
"learning_rate_type": trial.suggest_categorical(
"learning_rate_type", ["constant", "adaptive"]
),
"alpha": trial.suggest_float("alpha", 1e-8, 10.0, log=True),
"seed": self.seed,
"ml_task": self.ml_task,
}
model = Algorithm(params)
model.fit(self.X_train, self.y_train, sample_weight=self.sample_weight)
preds = model.predict(self.X_validation)
score = self.eval_metric(self.y_validation, preds)
if Metric.optimize_negative(self.eval_metric.name):
score *= -1.0
except optuna.exceptions.TrialPruned as e:
raise e
except Exception as e:
print("Exception in NeuralNetworkObjective", str(e))
return None
return score
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_utils/test_compute_additional_metrics.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import numpy as np
from supervised.algorithms.registry import BINARY_CLASSIFICATION, REGRESSION
from supervised.utils.additional_metrics import AdditionalMetrics
class ComputeAdditionalMetricsTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_compute(self):
target = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1])
pred = np.array([0.1, 0.8, 0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.1, 0.8, 0.8])
info = AdditionalMetrics.compute(target, pred, None, BINARY_CLASSIFICATION)
details = info["metric_details"]
max_metrics = info["max_metrics"]
conf = info["confusion_matrix"]
self.assertEqual(conf.iloc[0, 0], 3)
self.assertEqual(conf.iloc[1, 1], 3)
self.assertTrue(details is not None)
self.assertTrue(max_metrics is not None)
def test_compute_f1(self):
target = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1])
pred = np.array([0.01, 0.2, 0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.8, 0.8, 0.8])
info = AdditionalMetrics.compute(target, pred, None, BINARY_CLASSIFICATION)
details = info["metric_details"]
max_metrics = info["max_metrics"]
conf = info["confusion_matrix"]
self.assertEqual(max_metrics["f1"]["score"], 1)
self.assertTrue(details is not None)
self.assertTrue(conf is not None)
def test_compute_for_regression(self):
target = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1])
pred = np.array([0.01, 0.2, 0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.8, 0.8, 0.8])
info = AdditionalMetrics.compute(target, pred, None, REGRESSION)
all_metrics = list(info["max_metrics"]["Metric"].values)
for m in ["MAE", "MSE", "RMSE", "R2"]:
self.assertTrue(m in all_metrics)
def test_compute_constant_preds(self):
target = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0])
pred = np.array([0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1])
info = AdditionalMetrics.compute(target, pred, None, BINARY_CLASSIFICATION)
details = info["metric_details"]
max_metrics = info["max_metrics"]
conf = info["confusion_matrix"]
self.assertTrue(max_metrics["f1"]["score"] < 1)
self.assertTrue(max_metrics["mcc"]["score"] < 1)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_fairness/test_regression.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import shutil
import unittest
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised import AutoML
class FairnessInRegressionTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "automl_fairness_testing"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_init(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(30, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 100, size=(30,))
S = pd.DataFrame({"sensitive": ["A", "B"] * 15})
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
model_time_limit=10,
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
explain_level=0,
train_ensemble=False,
stack_models=False,
validation_strategy={"validation_type": "split"},
start_random_models=1,
)
automl.fit(X, y, sensitive_features=S)
self.assertGreater(len(automl._models), 0)
sensitive_features_names = automl._models[0].get_sensitive_features_names()
self.assertEqual(len(sensitive_features_names), 1)
self.assertTrue("sensitive" in sensitive_features_names)
self.assertTrue(automl._models[0].get_fairness_metric("sensitive") is not None)
self.assertTrue(len(automl._models[0].get_fairness_optimization()) > 1)
self.assertTrue(automl._models[0].get_worst_fairness() is not None)
self.assertTrue(automl._models[0].get_best_fairness() is not None)
def test_two_sensitive_features(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(30, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 100, size=(30,))
S = pd.DataFrame(
{
"sensitive_1": ["White", "Black"] * 15,
"sensitive_2": ["Male", "Female"] * 15,
}
)
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
model_time_limit=10,
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
explain_level=0,
train_ensemble=False,
stack_models=False,
start_random_models=1,
)
automl.fit(X, y, sensitive_features=S)
self.assertGreater(len(automl._models), 0)
sensitive_features_names = automl._models[0].get_sensitive_features_names()
self.assertEqual(len(sensitive_features_names), 2)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_tuner/test_time_controller.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import time
import unittest
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from supervised.tuner.time_controller import TimeController
class TimeControllerTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_to_and_from_json(self):
tc = TimeController(
start_time=time.time(),
total_time_limit=10,
model_time_limit=None,
steps=["simple_algorithms"],
algorithms=["Baseline"],
)
tc.log_time("1_Baseline", "Baseline", "simple_algorithms", 123.1)
tc2 = TimeController.from_json(tc.to_json())
assert_almost_equal(tc2.step_spend("simple_algorithms"), 123.1)
assert_almost_equal(tc2.model_spend("Baseline"), 123.1)
def test_enough_time_for_stacking(self):
for t in [5, 10, 20]:
tc = TimeController(
start_time=time.time(),
total_time_limit=100,
model_time_limit=None,
steps=[
"default_algorithms",
"not_so_random",
"golden_features",
"insert_random_feature",
"features_selection",
"hill_climbing_1",
"hill_climbing_3",
"hill_climbing_5",
"ensemble",
"stack",
"ensemble_stacked",
],
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
)
tc.log_time("1_Xgboost", "Xgboost", "default_algorithms", t)
tc.log_time("2_Xgboost", "Xgboost", "not_so_random", t)
tc.log_time("3_Xgboost", "Xgboost", "insert_random_feature", t)
tc.log_time("4_Xgboost", "Xgboost", "features_selection", t)
tc.log_time("5_Xgboost", "Xgboost", "hill_climbing_1", t)
tc.log_time("6_Xgboost", "Xgboost", "hill_climbing_2", t)
tc.log_time("7_Xgboost", "Xgboost", "hill_climbing_3", t)
tc._start_time = time.time() - 7 * t
assert_almost_equal(tc.already_spend(), 7 * t)
if t < 20:
self.assertTrue(tc.enough_time("Xgboost", "stack"))
else:
self.assertFalse(tc.enough_time("Xgboost", "stack"))
self.assertTrue(tc.enough_time("Ensemble_Stacked", "ensemble_stacked"))
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/algorithms/registry.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
# tasks that can be handled by the package
BINARY_CLASSIFICATION = "binary_classification"
MULTICLASS_CLASSIFICATION = "multiclass_classification"
REGRESSION = "regression"
class AlgorithmsRegistry:
registry = {
BINARY_CLASSIFICATION: {},
MULTICLASS_CLASSIFICATION: {},
REGRESSION: {},
}
@staticmethod
def add(
task_name,
model_class,
model_params,
required_preprocessing,
additional,
default_params,
):
model_information = {
"class": model_class,
"params": model_params,
"required_preprocessing": required_preprocessing,
"additional": additional,
"default_params": default_params,
}
AlgorithmsRegistry.registry[task_name][
model_class.algorithm_short_name
] = model_information
@staticmethod
def get_supported_ml_tasks():
return AlgorithmsRegistry.registry.keys()
@staticmethod
def get_algorithm_class(ml_task, algorithm_name):
return AlgorithmsRegistry.registry[ml_task][algorithm_name]["class"]
@staticmethod
def get_long_name(ml_task, algorithm_name):
return AlgorithmsRegistry.registry[ml_task][algorithm_name][
"class"
].algorithm_name
@staticmethod
def get_max_rows_limit(ml_task, algorithm_name):
return AlgorithmsRegistry.registry[ml_task][algorithm_name]["additional"][
"max_rows_limit"
]
@staticmethod
def get_max_cols_limit(ml_task, algorithm_name):
return AlgorithmsRegistry.registry[ml_task][algorithm_name]["additional"][
"max_cols_limit"
]
@staticmethod
def get_eval_metric(algorithm_name, ml_task, automl_eval_metric):
if algorithm_name == "Xgboost":
return xgboost_eval_metric(ml_task, automl_eval_metric)
return automl_eval_metric
# Import algorithm to be registered
import supervised.algorithms.baseline
import supervised.algorithms.catboost
import supervised.algorithms.decision_tree
import supervised.algorithms.extra_trees
import supervised.algorithms.knn
import supervised.algorithms.lightgbm
import supervised.algorithms.linear
import supervised.algorithms.nn
import supervised.algorithms.random_forest
import supervised.algorithms.xgboost
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/tuner/hill_climbing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import copy
import numpy as np
from supervised.algorithms.registry import AlgorithmsRegistry
class HillClimbing:
"""
Example params are in JSON format:
{
"booster": ["gbtree", "gblinear"],
"objective": ["binary:logistic"],
"eval_metric": ["auc", "logloss"],
"eta": [0.0025, 0.005, 0.0075, 0.01, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1]
}
"""
@staticmethod
def get(params, ml_task, seed=1):
np.random.seed(seed)
keys = list(params.keys())
for k in [
"num_class",
"model_type",
"seed",
"ml_task",
"explain_level",
"model_architecture_json",
"n_jobs",
"metric",
"eval_metric",
"custom_eval_metric_name",
"eval_metric_name",
]:
if k in keys:
keys.remove(k)
model_type = params["model_type"]
if model_type == "Baseline":
return [None, None]
model_info = AlgorithmsRegistry.registry[ml_task][model_type]
model_params = model_info["params"]
permuted_keys = np.random.permutation(keys)
key_to_update = None
values = None
for key_to_update in permuted_keys:
if key_to_update not in model_params:
continue
values = model_params[key_to_update]
if len(values) > 1:
break
if values is None:
return [None, None]
left, right = None, None
for i, v in enumerate(values):
if v == params[key_to_update]:
if i + 1 < len(values):
right = values[i + 1]
if i - 1 >= 0:
left = values[i - 1]
params_1, params_2 = None, None
if left is not None:
params_1 = copy.deepcopy(params)
params_1[key_to_update] = left
if right is not None:
params_2 = copy.deepcopy(params)
params_2[key_to_update] = right
if params_1 is not None and "model_architecture_json" in params_1:
del params_1["model_architecture_json"]
if params_2 is not None and "model_architecture_json" in params_2:
del params_2["model_architecture_json"]
return [params_1, params_2]
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/tuner/data_info.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from supervised.algorithms.registry import (
BINARY_CLASSIFICATION,
MULTICLASS_CLASSIFICATION,
REGRESSION,
)
from supervised.preprocessing.encoding_selector import EncodingSelector
from supervised.preprocessing.preprocessing_utils import PreprocessingUtils
class DataInfo:
@staticmethod
def compute(X, y, machinelearning_task):
columns_info = {}
for col in X.columns:
columns_info[col] = []
#
empty_column = np.sum(pd.isnull(X[col]) == True) == X.shape[0]
if empty_column:
columns_info[col] += ["empty_column"]
continue
#
constant_column = len(np.unique(X.loc[~pd.isnull(X[col]), col])) == 1
if constant_column:
columns_info[col] += ["constant_column"]
continue
#
if PreprocessingUtils.is_na(X[col]):
columns_info[col] += ["missing_values"]
#
if PreprocessingUtils.is_categorical(X[col]):
columns_info[col] += ["categorical"]
columns_info[col] += [EncodingSelector.get(X, y, col)]
elif PreprocessingUtils.is_datetime(X[col]):
columns_info[col] += ["datetime_transform"]
elif PreprocessingUtils.is_text(X[col]):
columns_info[col] = ["text_transform"] # override other transforms
else:
# numeric type, check if scale needed
if PreprocessingUtils.is_scale_needed(X[col]):
columns_info[col] += ["scale"]
target_info = []
if machinelearning_task == BINARY_CLASSIFICATION:
if not PreprocessingUtils.is_0_1(y):
target_info += ["convert_0_1"]
if machinelearning_task == REGRESSION:
if PreprocessingUtils.is_log_scale_needed(y):
target_info += ["scale_log"]
elif PreprocessingUtils.is_scale_needed(y):
target_info += ["scale"]
num_class = None
if machinelearning_task == MULTICLASS_CLASSIFICATION:
num_class = PreprocessingUtils.num_class(y)
return {
"columns_info": columns_info,
"target_info": target_info,
"num_class": num_class,
}
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_dir_change.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import os
import shutil
import unittest
import numpy as np
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from sklearn import datasets
from supervised import AutoML
class AutoMLDirChangeTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir_a = "automl_testing_A"
automl_dir_b = "automl_testing_B"
automl_dir = "automl_testing"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir_a, ignore_errors=True)
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir_b, ignore_errors=True)
def create_dir(self, dir_path):
if not os.path.exists(dir_path):
try:
os.mkdir(dir_path)
except Exception as e:
pass
def test_create_report_after_dir_change(self):
#
# test for https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised/issues/384
#
self.create_dir(self.automl_dir_a)
self.create_dir(self.automl_dir_b)
path_a = os.path.join(self.automl_dir_a, self.automl_dir)
path_b = os.path.join(self.automl_dir_b, self.automl_dir)
X = np.random.uniform(size=(30, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(30,))
automl = AutoML(results_path=path_a, algorithms=["Baseline"], explain_level=0)
automl.fit(X, y)
shutil.move(path_a, path_b)
automl2 = AutoML(
results_path=path_b,
)
automl2.report()
def test_compute_predictions_after_dir_change(self):
#
# test for https://github.com/mljar/mljar-supervised/issues/384
#
self.create_dir(self.automl_dir_a)
self.create_dir(self.automl_dir_b)
path_a = os.path.join(self.automl_dir_a, self.automl_dir)
path_b = os.path.join(self.automl_dir_b, self.automl_dir)
X, y = datasets.make_regression(
n_samples=100,
n_features=5,
n_informative=4,
n_targets=1,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
automl = AutoML(
results_path=path_a,
explain_level=0,
ml_task="regression",
total_time_limit=10,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
p = automl.predict(X[:3])
shutil.move(path_a, path_b)
automl2 = AutoML(
results_path=path_b,
)
p2 = automl2.predict(X[:3])
for i in range(3):
assert_almost_equal(p[i], p2[i])
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_preprocessing/test_scale.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from supervised.preprocessing.scale import Scale
class ScaleTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_fit_log_and_normal(self):
# training data
d = {
"col1": [12, 13, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8000, 9000, 10000.0],
"col2": [21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30.0],
"col3": [12, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8000, 9000, 10000.0],
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
scale = Scale(["col1", "col3"], scale_method=Scale.SCALE_LOG_AND_NORMAL)
scale.fit(df)
df = scale.transform(df)
val = float(df["col1"][0])
assert_almost_equal(np.mean(df["col1"]), 0)
self.assertTrue(
df["col1"][0] + 0.01 < df["col1"][1]
) # in case of wrong scaling the small values will be squeezed
df = scale.inverse_transform(df)
scale2 = Scale()
scale_params = scale.to_json()
scale2.from_json(scale_params)
df = scale2.transform(df)
assert_almost_equal(df["col1"][0], val)
def test_fit(self):
# training data
d = {
"col1": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10.0],
"col2": [21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30.0],
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
scale = Scale(["col1"])
scale.fit(df)
df = scale.transform(df)
assert_almost_equal(np.mean(df["col1"]), 0)
assert_almost_equal(np.mean(df["col2"]), 25.5)
df = scale.inverse_transform(df)
assert_almost_equal(df["col1"][0], 1)
assert_almost_equal(df["col1"][1], 2)
def test_to_and_from_json(self):
# training data
d = {
"col1": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8.0, 9, 10],
"col2": [21, 22.0, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30],
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
scale = Scale(["col1"])
scale.fit(df)
# do not transform
assert_almost_equal(np.mean(df["col1"]), 5.5)
assert_almost_equal(np.mean(df["col2"]), 25.5)
# to and from json
json_data = scale.to_json()
scale2 = Scale()
scale2.from_json(json_data)
# transform with loaded scaler
df = scale2.transform(df)
assert_almost_equal(np.mean(df["col1"]), 0)
assert_almost_equal(np.mean(df["col2"]), 25.5)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_utils/test_metric.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import numpy as np
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from supervised.utils.metric import Metric
from supervised.utils.metric import UserDefinedEvalMetric
class MetricTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_create(self):
params = {"name": "logloss"}
m = Metric(params)
y_true = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
y_predicted = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
score = m(y_true, y_predicted)
self.assertTrue(score < 0.1)
y_true = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
y_predicted = np.array([1, 1, 0, 0])
score = m(y_true, y_predicted)
self.assertTrue(score > 1.0)
def test_metric_improvement(self):
params = {"name": "logloss"}
m = Metric(params)
y_true = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
y_predicted = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1])
score_1 = m(y_true, y_predicted)
y_true = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
y_predicted = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
score_2 = m(y_true, y_predicted)
self.assertTrue(m.improvement(score_1, score_2))
def test_sample_weight(self):
metrics = ["logloss", "auc", "acc", "rmse", "mse", "mae", "r2", "mape"]
for m in metrics:
metric = Metric({"name": m})
y_true = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
y_predicted = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1])
sample_weight = np.array([1, 1, 1, 1])
score_1 = metric(y_true, y_predicted)
score_2 = metric(y_true, y_predicted, sample_weight)
assert_almost_equal(score_1, score_2)
def test_r2_metric(self):
params = {"name": "r2"}
m = Metric(params)
y_true = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
y_predicted = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
score = m(y_true, y_predicted)
self.assertEqual(score, -1.0) # negative r2
def test_mape_metric(self):
params = {"name": "mape"}
m = Metric(params)
y_true = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
y_predicted = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
score = m(y_true, y_predicted)
self.assertEqual(score, 0.0)
def test_user_defined_metric(self):
def custom(x, y, sample_weight=None):
return np.sum(x + y)
UserDefinedEvalMetric().set_metric(custom)
params = {"name": "user_defined_metric"}
m = Metric(params)
a = np.array([1, 1, 1])
score = m(a, a)
self.assertEqual(score, 6)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_joblib_version.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import json
import os
import shutil
import unittest
import joblib
import numpy as np
from supervised import AutoML
from supervised.exceptions import AutoMLException
class TestJoblibVersion(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "TestJoblibVersion"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_joblib_good_version(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(60, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(60,))
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
model_time_limit=10,
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
mode="Explain",
explain_level=0,
start_random_models=1,
hill_climbing_steps=0,
top_models_to_improve=0,
kmeans_features=False,
golden_features=False,
features_selection=False,
boost_on_errors=False,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
# Test if joblib is in json
json_path = os.path.join(self.automl_dir, "1_Default_Xgboost", "framework.json")
with open(json_path) as file:
frame = json.load(file)
json_version = frame["joblib_version"]
expected_result = joblib.__version__
self.assertEqual(expected_result, json_version)
def test_joblib_wrong_version(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(60, 2))
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(60,))
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
model_time_limit=10,
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
mode="Explain",
explain_level=0,
start_random_models=1,
hill_climbing_steps=0,
top_models_to_improve=0,
kmeans_features=False,
golden_features=False,
features_selection=False,
boost_on_errors=False,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
json_path = os.path.join(self.automl_dir, "1_Default_Xgboost", "framework.json")
with open(json_path) as file:
frame = json.load(file)
# Injection of wrong joblib version
frame["joblib_version"] = "0.2.0"
with open(json_path, "w") as file:
json.dump(frame, file)
with self.assertRaises(AutoMLException):
automl_2 = AutoML(results_path=self.automl_dir)
automl_2.predict(X)
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/algorithms/baseline.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
import sklearn
from sklearn.base import ClassifierMixin, RegressorMixin
from sklearn.dummy import DummyClassifier, DummyRegressor
from supervised.algorithms.registry import (
BINARY_CLASSIFICATION,
MULTICLASS_CLASSIFICATION,
REGRESSION,
AlgorithmsRegistry,
)
from supervised.algorithms.sklearn import SklearnAlgorithm
from supervised.utils.config import LOG_LEVEL
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.setLevel(LOG_LEVEL)
class BaselineClassifierAlgorithm(ClassifierMixin, SklearnAlgorithm):
algorithm_name = "Baseline Classifier"
algorithm_short_name = "Baseline"
def __init__(self, params):
super(BaselineClassifierAlgorithm, self).__init__(params)
logger.debug("BaselineClassifierAlgorithm.__init__")
self.library_version = sklearn.__version__
self.max_iters = additional.get("max_steps", 1)
self.model = DummyClassifier(
strategy="prior", random_state=params.get("seed", 1)
)
def file_extension(self):
return "baseline"
def is_fitted(self):
return (
hasattr(self.model, "n_outputs_")
and self.model.n_outputs_ is not None
and self.model.n_outputs_ > 0
)
class BaselineRegressorAlgorithm(RegressorMixin, SklearnAlgorithm):
algorithm_name = "Baseline Regressor"
algorithm_short_name = "Baseline"
def __init__(self, params):
super(BaselineRegressorAlgorithm, self).__init__(params)
logger.debug("BaselineRegressorAlgorithm.__init__")
self.library_version = sklearn.__version__
self.max_iters = additional.get("max_steps", 1)
self.model = DummyRegressor(strategy="mean")
def file_extension(self):
return "baseline"
def is_fitted(self):
return (
hasattr(self.model, "n_outputs_")
and self.model.n_outputs_ is not None
and self.model.n_outputs_ > 0
)
additional = {"max_steps": 1, "max_rows_limit": None, "max_cols_limit": None}
required_preprocessing = ["target_as_integer"]
AlgorithmsRegistry.add(
BINARY_CLASSIFICATION,
BaselineClassifierAlgorithm,
{},
required_preprocessing,
additional,
{},
)
AlgorithmsRegistry.add(
MULTICLASS_CLASSIFICATION,
BaselineClassifierAlgorithm,
{},
required_preprocessing,
additional,
{},
)
AlgorithmsRegistry.add(REGRESSION, BaselineRegressorAlgorithm, {}, {}, additional, {})
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/tuner/optuna/extra_trees.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import optuna
from supervised.algorithms.extra_trees import (
ExtraTreesAlgorithm,
ExtraTreesRegressorAlgorithm,
)
from supervised.algorithms.registry import (
REGRESSION,
)
from supervised.utils.metric import Metric
EPS = 1e-8
class ExtraTreesObjective:
def __init__(
self,
ml_task,
X_train,
y_train,
sample_weight,
X_validation,
y_validation,
sample_weight_validation,
eval_metric,
n_jobs,
random_state,
):
self.ml_task = ml_task
self.X_train = X_train
self.y_train = y_train
self.sample_weight = sample_weight
self.X_validation = X_validation
self.y_validation = y_validation
self.eval_metric = eval_metric
self.n_jobs = n_jobs
self.objective = "squared_error" if ml_task == REGRESSION else "gini"
self.max_steps = 10 # ET is trained in steps 100 trees each
self.seed = random_state
def __call__(self, trial):
try:
Algorithm = (
ExtraTreesRegressorAlgorithm
if self.ml_task == REGRESSION
else ExtraTreesAlgorithm
)
self.objective = (
"squared_error"
if self.ml_task == REGRESSION
else trial.suggest_categorical("criterion", ["gini", "entropy"])
)
params = {
"max_steps": self.max_steps,
"criterion": self.objective,
"max_depth": trial.suggest_int("max_depth", 2, 32),
"min_samples_split": trial.suggest_int("min_samples_split", 2, 100),
"min_samples_leaf": trial.suggest_int("min_samples_leaf", 1, 100),
"max_features": trial.suggest_float("max_features", 0.01, 1),
"n_jobs": self.n_jobs,
"seed": self.seed,
"ml_task": self.ml_task,
}
model = Algorithm(params)
model.fit(self.X_train, self.y_train, sample_weight=self.sample_weight)
preds = model.predict(self.X_validation)
score = self.eval_metric(self.y_validation, preds)
if Metric.optimize_negative(self.eval_metric.name):
score *= -1.0
except optuna.exceptions.TrialPruned as e:
raise e
except Exception as e:
print("Exception in ExtraTreesObjective", str(e))
return None
return score
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/tuner/optuna/random_forest.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import optuna
from supervised.algorithms.random_forest import (
RandomForestAlgorithm,
RandomForestRegressorAlgorithm,
)
from supervised.algorithms.registry import (
REGRESSION,
)
from supervised.utils.metric import Metric
class RandomForestObjective:
def __init__(
self,
ml_task,
X_train,
y_train,
sample_weight,
X_validation,
y_validation,
sample_weight_validation,
eval_metric,
n_jobs,
random_state,
):
self.ml_task = ml_task
self.X_train = X_train
self.y_train = y_train
self.sample_weight = sample_weight
self.X_validation = X_validation
self.y_validation = y_validation
self.eval_metric = eval_metric
self.n_jobs = n_jobs
self.objective = "squared_error" if ml_task == REGRESSION else "gini"
self.max_steps = 10 # RF is trained in steps 100 trees each
self.seed = random_state
def __call__(self, trial):
try:
Algorithm = (
RandomForestRegressorAlgorithm
if self.ml_task == REGRESSION
else RandomForestAlgorithm
)
self.objective = (
"squared_error"
if self.ml_task == REGRESSION
else trial.suggest_categorical("criterion", ["gini", "entropy"])
)
params = {
"max_steps": self.max_steps,
"criterion": self.objective,
"max_depth": trial.suggest_int("max_depth", 2, 32),
"min_samples_split": trial.suggest_int("min_samples_split", 2, 100),
"min_samples_leaf": trial.suggest_int("min_samples_leaf", 1, 100),
"max_features": trial.suggest_float("max_features", 0.01, 1),
"n_jobs": self.n_jobs,
"seed": self.seed,
"ml_task": self.ml_task,
}
model = Algorithm(params)
model.fit(self.X_train, self.y_train, sample_weight=self.sample_weight)
preds = model.predict(self.X_validation)
score = self.eval_metric(self.y_validation, preds)
if Metric.optimize_negative(self.eval_metric.name):
score *= -1.0
except optuna.exceptions.TrialPruned as e:
raise e
except Exception as e:
print("Exception in RandomForestObjective", str(e))
return None
return score
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_tuner/test_hill_climbing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
from supervised.tuner.mljar_tuner import MljarTuner
class ModelMock:
def __init__(self, name, model_type, final_loss, params):
self.name = name
self.model_type = model_type
self.final_loss = final_loss
self.params = params
def get_name(self):
return self.name
def get_type(self):
return self.model_type
def get_final_loss(self):
return self.final_loss
def get_train_time(self):
return 0.1
class TunerHillClimbingTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_hill_climbing(self):
models = []
models += [
ModelMock(
"121_RandomForest",
"Random Forest",
0.1,
{
"learner": {"max_features": 0.4, "model_type": "Random Forest"},
"preprocessing": {},
"validation_strategy": {},
},
)
]
models += [
ModelMock(
"1_RandomForest",
"Random Forest",
0.1,
{
"learner": {"max_features": 0.4, "model_type": "Random Forest"},
"preprocessing": {},
"validation_strategy": {},
},
)
]
tuner = MljarTuner(
{
"start_random_models": 0,
"hill_climbing_steps": 1,
"top_models_to_improve": 2,
},
algorithms=["Random Foresrt"],
ml_task="binary_classification",
eval_metric="logloss",
validation_strategy={},
explain_level=2,
data_info={"columns_info": [], "target_info": []},
golden_features=False,
features_selection=False,
train_ensemble=False,
stack_models=False,
adjust_validation=False,
boost_on_errors=False,
kmeans_features=False,
mix_encoding=False,
optuna_time_budget=None,
optuna_init_params={},
optuna_verbose=True,
n_jobs=1,
seed=12,
)
ind = 121
score = 0.1
for _ in range(5):
for p in tuner.get_hill_climbing_params(models):
models += [ModelMock(p["name"], "Random Forest", score, p)]
score *= 0.1
self.assertTrue(int(p["name"].split("_")[0]) > ind)
ind += 1
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/preprocessing/text_transformer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import warnings
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
class TextTransformer(object):
def __init__(self):
self._new_columns = []
self._old_column = None
self._max_features = 100
self._vectorizer = None
def fit(self, X, column):
self._old_column = column
self._vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(
analyzer="word",
stop_words="english",
lowercase=True,
max_features=self._max_features,
)
x = X[column][~pd.isnull(X[column])]
self._vectorizer.fit(x)
for f in list(self._vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()):
new_col = self._old_column + "_" + f
self._new_columns += [new_col]
def transform(self, X):
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter(
action="ignore", category=pd.errors.PerformanceWarning
)
ii = ~pd.isnull(X[self._old_column])
x = X[self._old_column][ii]
vect = self._vectorizer.transform(x)
for f in self._new_columns:
X[f] = 0.0
X.loc[ii, self._new_columns] = vect.toarray()
X.drop(self._old_column, axis=1, inplace=True)
return X
def to_json(self):
for k in self._vectorizer.vocabulary_.keys():
self._vectorizer.vocabulary_[k] = int(self._vectorizer.vocabulary_[k])
data_json = {
"new_columns": list(self._new_columns),
"old_column": self._old_column,
"vocabulary": self._vectorizer.vocabulary_,
"fixed_vocabulary": self._vectorizer.fixed_vocabulary_,
"idf": list(self._vectorizer.idf_),
}
return data_json
def from_json(self, data_json):
self._new_columns = data_json.get("new_columns", None)
self._old_column = data_json.get("old_column", None)
vocabulary = data_json.get("vocabulary")
fixed_vocabulary = data_json.get("fixed_vocabulary")
idf = data_json.get("idf")
if vocabulary is not None and fixed_vocabulary is not None and idf is not None:
self._vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(
analyzer="word",
stop_words="english",
lowercase=True,
max_features=self._max_features,
)
self._vectorizer.vocabulary_ = vocabulary
self._vectorizer.fixed_vocabulary_ = fixed_vocabulary
self._vectorizer.idf_ = np.array(idf)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_algorithms/test_baseline.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import os
import tempfile
import unittest
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from sklearn import datasets
from supervised.algorithms.baseline import (
BaselineClassifierAlgorithm,
BaselineRegressorAlgorithm,
)
from supervised.utils.metric import Metric
class BaselineTest(unittest.TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
cls.X, cls.y = datasets.make_regression(
n_samples=100,
n_features=5,
n_informative=4,
n_targets=1,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
def test_reproduce_fit_regression(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "rmse"})
prev_loss = None
for _ in range(3):
model = BaselineRegressorAlgorithm({"ml_task": "regression"})
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = model.predict(self.X)
loss = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
if prev_loss is not None:
assert_almost_equal(prev_loss, loss)
prev_loss = loss
def test_reproduce_fit_bin_class(self):
X, y = datasets.make_classification(
n_samples=100,
n_features=5,
n_informative=4,
n_redundant=1,
n_classes=2,
n_clusters_per_class=3,
n_repeated=0,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
metric = Metric({"name": "logloss"})
prev_loss = None
for _ in range(3):
model = BaselineClassifierAlgorithm({"ml_task": "binary_classification"})
model.fit(X, y)
y_predicted = model.predict(X)
loss = metric(y, y_predicted)
if prev_loss is not None:
assert_almost_equal(prev_loss, loss)
prev_loss = loss
def test_save_and_load(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "rmse"})
dt = BaselineRegressorAlgorithm({"ml_task": "regression"})
dt.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = dt.predict(self.X)
loss = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
filename = os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), os.urandom(12).hex())
dt.save(filename)
dt2 = BaselineRegressorAlgorithm({"ml_task": "regression"})
dt2.load(filename)
# Finished with the file, delete it
os.remove(filename)
y_predicted = dt2.predict(self.X)
loss2 = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
assert_almost_equal(loss, loss2)
def test_is_fitted(self):
model = BaselineRegressorAlgorithm({"ml_task": "regression"})
self.assertFalse(model.is_fitted())
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
self.assertTrue(model.is_fitted())
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/preprocessing/label_binarizer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
class LabelBinarizer(object):
def __init__(self):
self._new_columns = []
self._uniq_values = None
self._old_column = None
self._old_column_dtype = None
def fit(self, X, column):
self._old_column = column
self._old_column_dtype = str(X[column].dtype)
self._uniq_values = np.unique(X[column].values)
# self._uniq_values = [str(u) for u in self._uniq_values]
if len(self._uniq_values) == 2:
self._new_columns.append(column + "_" + str(self._uniq_values[1]))
else:
for v in self._uniq_values:
self._new_columns.append(column + "_" + str(v))
def transform(self, X, column):
if len(self._uniq_values) == 2:
X[column + "_" + str(self._uniq_values[1])] = (
X[column] == self._uniq_values[1]
).astype(int)
else:
for v in self._uniq_values:
X[column + "_" + str(v)] = (X[column] == v).astype(int)
X.drop(column, axis=1, inplace=True)
return X
def inverse_transform(self, X):
if self._old_column is None:
return X
old_col = (X[self._new_columns[0]] * 0).astype(self._old_column_dtype)
for unique_value in self._uniq_values:
new_col = f"{self._old_column}_{unique_value}"
if new_col not in self._new_columns:
old_col[:] = unique_value
else:
old_col[X[new_col] == 1] = unique_value
X[self._old_column] = old_col
X.drop(self._new_columns, axis=1, inplace=True)
return X
def to_json(self):
self._uniq_values = [str(i) for i in list(self._uniq_values)]
data_json = {
"new_columns": list(self._new_columns),
"unique_values": self._uniq_values,
"old_column": self._old_column,
"old_column_dtype": self._old_column_dtype,
}
if (
"True" in self._uniq_values
and "False" in self._uniq_values
and len(self._uniq_values) == 2
):
self._uniq_values = [False, True]
return data_json
def from_json(self, data_json):
self._new_columns = data_json.get("new_columns", None)
self._uniq_values = data_json.get("unique_values", None)
self._old_column = data_json.get("old_column", None)
self._old_column_dtype = data_json.get("old_column_dtype", None)
if (
"True" in self._uniq_values
and "False" in self._uniq_values
and len(self._uniq_values) == 2
):
self._uniq_values = [False, True]
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/data/iris_classes_missing_values_missing_target.csv:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```
feature_1,feature_2,feature_3,feature_4,class
5.1,3.5,1.4,0.2,1
4.9,3.0,1.4,0.2,1
4.7,3.2,1.3,,1
4.6,3.1,1.5,,1
5.0,3.6,1.4,0.2,1
,3.9,1.7,0.4,1
4.6,3.4,1.4,0.3,1
5.0,3.4,1.5,0.2,1
4.4,,1.4,0.2,1
4.9,3.1,1.5,0.1,1
5.4,3.7,1.5,0.2,1
4.8,3.4,,0.2,1
4.8,3.0,1.4,0.1,1
4.3,3.0,1.1,0.1,1
5.8,4.0,1.2,0.2,1
5.7,4.4,1.5,0.4,1
5.4,3.9,1.3,0.4,1
5.1,3.5,1.4,0.3,
5.7,3.8,1.7,0.3,1
5.1,3.8,1.5,0.3,1
5.4,3.4,1.7,0.2,1
5.1,3.7,1.5,0.4,1
4.6,3.6,1.0,0.2,1
5.1,3.3,1.7,0.5,1
4.8,3.4,1.9,0.2,1
5.0,3.0,1.6,0.2,1
5.0,3.4,1.6,0.4,1
5.2,3.5,1.5,0.2,1
5.2,3.4,1.4,0.2,1
4.7,3.2,1.6,0.2,1
4.8,3.1,1.6,0.2,1
5.4,3.4,1.5,0.4,1
5.2,4.1,1.5,0.1,1
5.5,4.2,1.4,0.2,1
4.9,3.1,1.5,0.1,1
5.0,3.2,1.2,0.2,1
5.5,3.5,1.3,0.2,1
4.9,3.1,1.5,0.1,1
4.4,3.0,1.3,0.2,1
5.1,3.4,1.5,0.2,1
5.0,3.5,1.3,0.3,1
4.5,2.3,1.3,0.3,1
4.4,3.2,1.3,0.2,1
5.0,3.5,1.6,0.6,1
5.1,3.8,1.9,0.4,1
4.8,3.0,1.4,0.3,1
5.1,3.8,1.6,0.2,1
4.6,3.2,1.4,0.2,1
5.3,3.7,1.5,0.2,1
5.0,3.3,1.4,0.2,1
7.0,3.2,4.7,1.4,2
6.4,3.2,4.5,1.5,2
6.9,3.1,4.9,1.5,
5.5,2.3,4.0,1.3,2
6.5,2.8,4.6,1.5,2
5.7,2.8,4.5,1.3,2
6.3,3.3,4.7,1.6,2
4.9,2.4,3.3,1.0,2
6.6,2.9,4.6,1.3,2
5.2,2.7,3.9,1.4,2
5.0,2.0,3.5,1.0,2
5.9,3.0,4.2,1.5,2
6.0,2.2,4.0,1.0,2
6.1,2.9,4.7,1.4,2
5.6,2.9,3.6,1.3,2
6.7,3.1,4.4,1.4,2
5.6,3.0,4.5,1.5,2
5.8,2.7,4.1,1.0,2
6.2,2.2,4.5,1.5,2
5.6,2.5,3.9,1.1,2
5.9,3.2,4.8,1.8,2
6.1,2.8,4.0,1.3,2
6.3,2.5,4.9,1.5,2
6.1,2.8,4.7,1.2,2
6.4,2.9,4.3,1.3,2
6.6,3.0,4.4,1.4,2
6.8,2.8,4.8,1.4,2
6.7,3.0,5.0,1.7,2
6.0,2.9,4.5,1.5,2
5.7,2.6,3.5,1.0,2
5.5,2.4,3.8,1.1,2
5.5,2.4,3.7,1.0,2
5.8,2.7,3.9,1.2,2
6.0,2.7,5.1,1.6,2
5.4,3.0,4.5,1.5,2
6.0,3.4,4.5,1.6,2
6.7,3.1,4.7,1.5,2
6.3,2.3,4.4,1.3,2
5.6,3.0,4.1,1.3,2
5.5,2.5,4.0,1.3,2
5.5,2.6,4.4,1.2,2
6.1,3.0,4.6,1.4,2
5.8,2.6,4.0,1.2,2
5.0,2.3,3.3,1.0,2
5.6,2.7,4.2,1.3,2
5.7,3.0,4.2,1.2,2
5.7,2.9,4.2,1.3,2
6.2,2.9,4.3,1.3,2
5.1,2.5,3.0,1.1,2
5.7,2.8,4.1,1.3,2
6.3,3.3,6.0,2.5,121
5.8,2.7,5.1,1.9,121
7.1,3.0,5.9,2.1,121
6.3,2.9,5.6,1.8,121
6.5,3.0,5.8,2.2,121
7.6,3.0,6.6,2.1,121
4.9,2.5,4.5,1.7,121
7.3,2.9,6.3,1.8,121
6.7,2.5,5.8,1.8,121
7.2,3.6,6.1,2.5,121
6.5,3.2,5.1,2.0,121
6.4,2.7,5.3,1.9,121
6.8,3.0,5.5,2.1,121
5.7,2.5,5.0,2.0,121
5.8,2.8,5.1,2.4,121
6.4,3.2,5.3,2.3,121
6.5,3.0,5.5,1.8,121
7.7,3.8,6.7,2.2,121
7.7,2.6,6.9,2.3,121
6.0,2.2,5.0,1.5,121
6.9,3.2,5.7,2.3,121
5.6,2.8,4.9,2.0,121
7.7,2.8,6.7,2.0,121
6.3,2.7,4.9,1.8,121
6.7,3.3,5.7,2.1,121
7.2,3.2,6.0,1.8,121
6.2,2.8,4.8,1.8,121
6.1,3.0,4.9,1.8,121
6.4,2.8,5.6,2.1,121
7.2,3.0,5.8,1.6,121
7.4,2.8,6.1,1.9,121
7.9,3.8,6.4,2.0,121
6.4,2.8,5.6,2.2,121
6.3,2.8,5.1,1.5,121
6.1,2.6,5.6,1.4,121
7.7,3.0,6.1,2.3,121
6.3,3.4,5.6,2.4,121
6.4,3.1,5.5,1.8,121
6.0,3.0,4.8,1.8,121
6.9,3.1,5.4,2.1,121
6.7,3.1,5.6,2.4,121
6.9,3.1,5.1,2.3,121
5.8,2.7,5.1,1.9,121
6.8,3.2,5.9,2.3,121
6.7,3.3,5.7,2.5,121
6.7,3.0,5.2,2.3,121
6.3,2.5,5.0,1.9,121
6.5,3.0,5.2,2.0,121
6.2,3.4,5.4,2.3,121
5.9,3.0,5.1,1.8,121
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_algorithms/test_knn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import unittest
import numpy as np
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from sklearn import datasets
from supervised.algorithms.knn import KNeighborsAlgorithm, KNeighborsRegressorAlgorithm
from supervised.utils.metric import Metric
class KNeighborsRegressorAlgorithmTest(unittest.TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
cls.X, cls.y = datasets.make_regression(
n_samples=100,
n_features=5,
n_informative=4,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0
)
def test_reproduce_fit(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "mse"})
params = {"seed": 1, "ml_task": "regression"}
prev_loss = None
for _ in range(2):
model = KNeighborsRegressorAlgorithm(params)
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = model.predict(self.X)
loss = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
if prev_loss is not None:
assert_almost_equal(prev_loss, loss)
prev_loss = loss
class KNeighborsAlgorithmTest(unittest.TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
cls.X, cls.y = datasets.make_classification(
n_samples=100,
n_features=5,
n_informative=4,
n_redundant=1,
n_classes=2,
n_clusters_per_class=3,
n_repeated=0,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
def test_reproduce_fit(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "logloss"})
params = {"seed": 1, "ml_task": "binary_classification"}
prev_loss = None
for _ in range(2):
model = KNeighborsAlgorithm(params)
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = model.predict(self.X)
loss = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
if prev_loss is not None:
assert_almost_equal(prev_loss, loss)
prev_loss = loss
def test_fit_predict(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "logloss"})
params = {"ml_task": "binary_classification"}
la = KNeighborsAlgorithm(params)
la.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = la.predict(self.X)
self.assertTrue(metric(self.y, y_predicted) < 0.6)
def test_is_fitted(self):
params = {"ml_task": "binary_classification"}
model = KNeighborsAlgorithm(params)
self.assertFalse(model.is_fitted())
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
self.assertTrue(model.is_fitted())
def test_classes_attribute(self):
params = {"ml_task": "binary_classification"}
model = KNeighborsAlgorithm(params)
model.fit(self.X,self.y)
try:
classes = model._classes
except AttributeError:
classes = None
self.assertTrue(np.array_equal(np.unique(self.y), classes))
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/utils/importance.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
import os
import warnings
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.inspection import permutation_importance
from supervised.algorithms.registry import (
BINARY_CLASSIFICATION,
MULTICLASS_CLASSIFICATION,
)
from supervised.utils.subsample import subsample
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
from supervised.utils.config import LOG_LEVEL
logger.setLevel(LOG_LEVEL)
from sklearn.metrics import log_loss, make_scorer
def log_loss_eps(y_true, y_pred):
ll = log_loss(y_true, y_pred)
return ll
log_loss_scorer = make_scorer(log_loss_eps, greater_is_better=False, response_method="predict_proba")
class PermutationImportance:
@staticmethod
def compute_and_plot(
model,
X_validation,
y_validation,
model_file_path,
learner_name,
metric_name=None,
ml_task=None,
n_jobs=-1,
):
# for scoring check https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/model_evaluation.html#scoring-parameter
if ml_task == BINARY_CLASSIFICATION:
scoring = log_loss_scorer
elif ml_task == MULTICLASS_CLASSIFICATION:
scoring = log_loss_scorer
else:
scoring = "neg_mean_squared_error"
try:
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
# subsample validation data to speed-up importance computation
# in the case of large number of columns, it can take a lot of time
rows, cols = X_validation.shape
if cols > 5000 and rows > 100:
X_vald, _, y_vald, _ = subsample(
X_validation, y_validation, train_size=100, ml_task=ml_task
)
elif cols > 50 and rows * cols > 200000 and rows > 1000:
X_vald, _, y_vald, _ = subsample(
X_validation, y_validation, train_size=1000, ml_task=ml_task
)
else:
X_vald = X_validation
y_vald = y_validation
importance = permutation_importance(
model,
X_vald,
y_vald,
scoring=scoring,
n_jobs=n_jobs,
random_state=12,
n_repeats=5, # default
)
sorted_idx = importance["importances_mean"].argsort()
# save detailed importance
df_imp = pd.DataFrame(
{
"feature": X_vald.columns[sorted_idx],
"mean_importance": importance["importances_mean"][sorted_idx],
}
)
df_imp.to_csv(
os.path.join(model_file_path, f"{learner_name}_importance.csv"),
index=False,
)
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
print("Problem during computing permutation importance. Skipping ...")
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_models_needed_for_predict.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import json
import os
import tempfile
import unittest
from supervised import AutoML
from supervised.exceptions import AutoMLException
class AutoMLModelsNeededForPredictTest(unittest.TestCase):
# models_needed_on_predict
def test_models_needed_on_predict(self):
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdir:
params = {
"saved": [
"model_1",
"model_2",
"model_3",
"unused_model",
"Ensemble",
"model_4_Stacked",
"Stacked_Ensemble",
],
"stacked": ["Ensemble", "model_1", "model_2"],
}
with open(os.path.join(tmpdir, "params.json"), "w") as fout:
fout.write(json.dumps(params))
os.mkdir(os.path.join(tmpdir, "Ensemble"))
with open(os.path.join(tmpdir, "Ensemble", "ensemble.json"), "w") as fout:
params = {
"selected_models": [
{"model": "model_2"},
{"model": "model_3"},
]
}
fout.write(json.dumps(params))
os.mkdir(os.path.join(tmpdir, "Stacked_Ensemble"))
with open(
os.path.join(tmpdir, "Stacked_Ensemble", "ensemble.json"), "w"
) as fout:
params = {
"selected_models": [
{"model": "Ensemble"},
{"model": "model_4_Stacked"},
]
}
fout.write(json.dumps(params))
automl = AutoML(results_path=tmpdir)
with self.assertRaises(AutoMLException) as context:
l = automl.models_needed_on_predict("missing_model")
l = automl.models_needed_on_predict("model_1")
self.assertTrue("model_1" in l)
self.assertTrue(len(l) == 1)
l = automl.models_needed_on_predict("model_3")
self.assertTrue("model_3" in l)
self.assertTrue(len(l) == 1)
l = automl.models_needed_on_predict("Ensemble")
self.assertTrue("model_2" in l)
self.assertTrue("model_3" in l)
self.assertTrue("Ensemble" in l)
self.assertTrue(len(l) == 3)
l = automl.models_needed_on_predict("model_4_Stacked")
self.assertTrue("model_1" in l)
self.assertTrue("model_2" in l)
self.assertTrue("model_3" in l)
self.assertTrue("Ensemble" in l)
self.assertTrue("model_4_Stacked" in l)
self.assertTrue(len(l) == 5)
l = automl.models_needed_on_predict("Stacked_Ensemble")
self.assertTrue("model_1" in l)
self.assertTrue("model_2" in l)
self.assertTrue("model_3" in l)
self.assertTrue("Ensemble" in l)
self.assertTrue("model_4_Stacked" in l)
self.assertTrue("Stacked_Ensemble" in l)
self.assertTrue(len(l) == 6)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_golden_features.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import json
import os
import shutil
import unittest
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import datasets
from supervised import AutoML
class AutoMLGoldenFeaturesTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "automl_tests"
rows = 50
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_no_golden_features(self):
N_COLS = 10
X, y = datasets.make_classification(
n_samples=100,
n_features=N_COLS,
n_informative=6,
n_redundant=1,
n_classes=2,
n_clusters_per_class=3,
n_repeated=0,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f{i}" for i in range(X.shape[1])])
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=50,
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
train_ensemble=False,
golden_features=False,
explain_level=0,
start_random_models=1,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
self.assertEqual(len(automl._models), 1)
def test_golden_features(self):
N_COLS = 10
X, y = datasets.make_classification(
n_samples=100,
n_features=N_COLS,
n_informative=6,
n_redundant=1,
n_classes=2,
n_clusters_per_class=3,
n_repeated=0,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f{i}" for i in range(X.shape[1])])
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=50,
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
train_ensemble=False,
golden_features=True,
explain_level=0,
start_random_models=1,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
self.assertEqual(len(automl._models), 2)
# there should be 10 golden features
with open(os.path.join(self.automl_dir, "golden_features.json")) as fin:
d = json.loads(fin.read())
self.assertEqual(len(d["new_features"]), 10)
def test_golden_features_count(self):
N_COLS = 10
X, y = datasets.make_classification(
n_samples=100,
n_features=N_COLS,
n_informative=6,
n_redundant=1,
n_classes=2,
n_clusters_per_class=3,
n_repeated=0,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f{i}" for i in range(X.shape[1])])
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=50,
algorithms=["Xgboost"],
train_ensemble=False,
golden_features=50,
explain_level=0,
start_random_models=1,
)
automl.fit(X, y)
self.assertEqual(len(automl._models), 2)
# there should be 50 golden features
with open(os.path.join(self.automl_dir, "golden_features.json")) as fin:
d = json.loads(fin.read())
self.assertEqual(len(d["new_features"]), 50)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_automl_sample_weight.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import shutil
import unittest
import numpy as np
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from sklearn import datasets
from supervised import AutoML
iris = datasets.load_iris()
housing = datasets.fetch_california_housing()
# limit data size for faster tests
housing.data = housing.data[:500]
housing.target = housing.target[:500]
breast_cancer = datasets.load_breast_cancer()
class AutoMLSampleWeightTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "AutoMLSampleWeightTest"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_iris_dataset_sample_weight(self):
"""Tests AutoML in the iris dataset (Multiclass classification)
without and with sample weight"""
model = AutoML(
explain_level=0, verbose=1, random_state=1, results_path=self.automl_dir
)
score_1 = model.fit(iris.data, iris.target).score(iris.data, iris.target)
self.assertGreater(score_1, 0.5)
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
model = AutoML(
explain_level=0, verbose=1, random_state=1, results_path=self.automl_dir
)
sample_weight = np.ones(iris.data.shape[0])
score_2 = model.fit(iris.data, iris.target, sample_weight=sample_weight).score(
iris.data, iris.target, sample_weight=sample_weight
)
assert_almost_equal(score_1, score_2)
def test_housing_dataset(self):
"""Tests AutoML in the housing dataset (Regression)
without and with sample weight"""
model = AutoML(
explain_level=0, verbose=1, random_state=1, results_path=self.automl_dir
)
score_1 = model.fit(housing.data, housing.target).score(
housing.data, housing.target
)
self.assertGreater(score_1, 0.5)
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
model = AutoML(
explain_level=0, verbose=1, random_state=1, results_path=self.automl_dir
)
sample_weight = np.ones(housing.data.shape[0])
score_2 = model.fit(
housing.data, housing.target, sample_weight=sample_weight
).score(housing.data, housing.target, sample_weight=sample_weight)
assert_almost_equal(score_1, score_2)
def test_breast_cancer_dataset(self):
"""Tests AutoML in the breast cancer (binary classification)
without and with sample weight"""
model = AutoML(
explain_level=0, verbose=1, random_state=1, results_path=self.automl_dir
)
score_1 = model.fit(breast_cancer.data, breast_cancer.target).score(
breast_cancer.data, breast_cancer.target
)
self.assertGreater(score_1, 0.5)
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
model = AutoML(
explain_level=0, verbose=1, random_state=1, results_path=self.automl_dir
)
sample_weight = np.ones(breast_cancer.data.shape[0])
score_2 = model.fit(
breast_cancer.data, breast_cancer.target, sample_weight=sample_weight
).score(breast_cancer.data, breast_cancer.target, sample_weight=sample_weight)
assert_almost_equal(score_1, score_2)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/callbacks/total_time_constraint.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
import time
import numpy as np
from supervised.callbacks.callback import Callback
from supervised.exceptions import NotTrainedException
from supervised.utils.config import LOG_LEVEL
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
log.setLevel(LOG_LEVEL)
class TotalTimeConstraint(Callback):
def __init__(self, params={}):
super(TotalTimeConstraint, self).__init__(params)
self.name = params.get("name", "total_time_constraint")
self.total_time_limit = params.get("total_time_limit")
self.total_time_start = params.get("total_time_start")
self.expected_learners_cnt = params.get("expected_learners_cnt", 1)
def on_learner_train_start(self, logs):
self.train_start_time = time.time()
def on_learner_train_end(self, logs):
if (
self.total_time_limit is not None
and len(self.learners) == 1
and self.expected_learners_cnt > 1
# just check for the first learner
# need to have more than 1 learner
# otherwise it is a finish of the training
):
one_fold_time = time.time() - self.train_start_time
estimate_all_folds = one_fold_time * self.expected_learners_cnt
total_elapsed_time = np.round(time.time() - self.total_time_start, 2)
# we need to add time for the rest of learners (assuming that all folds training time is the same)
estimate_elapsed_time = total_elapsed_time + one_fold_time * (
self.expected_learners_cnt - 1
)
if estimate_elapsed_time >= self.total_time_limit:
raise NotTrainedException(
"Stop training after the first fold. "
f"Time needed to train on the first fold {np.round(one_fold_time)} seconds. "
"The time estimate for training on all folds is larger than total_time_limit."
)
if (
self.total_time_limit is not None
and len(self.learners) < self.expected_learners_cnt
# dont stop for last learner, we are finishing anyway
):
total_elapsed_time = np.round(time.time() - self.total_time_start, 2)
if total_elapsed_time > self.total_time_limit + 600:
# add 10 minutes of margin
# margin is added because of unexpected time changes
# if training on each fold will be the same
# then the training will be stopped after first fold (above condition)
raise NotTrainedException(
"Force to stop the training. "
"Total time for AutoML training already exceeded."
)
def on_iteration_end(self, logs, predictions):
total_elapsed_time = np.round(time.time() - self.total_time_start, 2)
if self.total_time_limit is not None:
log.debug(
f"Total elapsed time {total_elapsed_time} seconds. "
+ f"Time left {np.round(self.total_time_limit - total_elapsed_time, 2)} seconds."
)
# not time left, stop now
if total_elapsed_time >= self.total_time_limit:
self.learner.stop_training = True
else:
log.debug(f"Total elapsed time {total_elapsed_time} seconds")
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_repeated_validation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import os
import shutil
import unittest
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import datasets
from supervised import AutoML
from supervised.algorithms.random_forest import additional
from supervised.utils.common import construct_learner_name
additional["max_steps"] = 1
additional["trees_in_step"] = 1
from supervised.algorithms.xgboost import additional
additional["max_rounds"] = 1
class AutoMLRepeatedValidationTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "AutoMLRepeatedValidationTest"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_repeated_kfold(self):
REPEATS = 3
FOLDS = 2
a = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=10,
algorithms=["Random Forest"],
train_ensemble=False,
validation_strategy={
"validation_type": "kfold",
"k_folds": FOLDS,
"repeats": REPEATS,
"shuffle": True,
"stratify": True,
},
start_random_models=1,
)
X, y = datasets.make_classification(
n_samples=100,
n_features=5,
n_informative=4,
n_redundant=1,
n_classes=2,
n_clusters_per_class=3,
n_repeated=0,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f_{i}" for i in range(X.shape[1])])
a.fit(X, y)
result_files = os.listdir(
os.path.join(self.automl_dir, "1_Default_RandomForest")
)
cnt = 0
for repeat in range(REPEATS):
for fold in range(FOLDS):
learner_name = construct_learner_name(fold, repeat, REPEATS)
self.assertTrue(f"{learner_name}.random_forest" in result_files)
self.assertTrue(f"{learner_name}_training.log" in result_files)
cnt += 1
self.assertTrue(cnt, 6)
def test_repeated_split(self):
REPEATS = 3
FOLDS = 1
a = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=10,
algorithms=["Random Forest"],
train_ensemble=False,
validation_strategy={
"validation_type": "split",
"repeats": REPEATS,
"shuffle": True,
"stratify": True,
},
start_random_models=1,
)
X, y = datasets.make_classification(
n_samples=100,
n_features=5,
n_informative=4,
n_redundant=1,
n_classes=2,
n_clusters_per_class=3,
n_repeated=0,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f"f_{i}" for i in range(X.shape[1])])
a.fit(X, y)
result_files = os.listdir(
os.path.join(self.automl_dir, "1_Default_RandomForest")
)
cnt = 0
for repeat in range(REPEATS):
for fold in range(FOLDS):
learner_name = construct_learner_name(fold, repeat, REPEATS)
self.assertTrue(f"{learner_name}.random_forest" in result_files)
self.assertTrue(f"{learner_name}_training.log" in result_files)
cnt += 1
self.assertTrue(cnt, 3)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/preprocessing/datetime_transformer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
class DateTimeTransformer(object):
def __init__(self):
self._new_columns = []
self._old_column = None
self._min_datetime = None
self._transforms = []
def fit(self, X, column):
self._old_column = column
self._min_datetime = np.min(X[column])
values = X[column].dt.year
if len(np.unique(values)) > 1:
self._transforms += ["year"]
new_column = column + "_Year"
self._new_columns += [new_column]
values = X[column].dt.month
if len(np.unique(values)) > 1:
self._transforms += ["month"]
new_column = column + "_Month"
self._new_columns += [new_column]
values = X[column].dt.day
if len(np.unique(values)) > 1:
self._transforms += ["day"]
new_column = column + "_Day"
self._new_columns += [new_column]
values = X[column].dt.weekday
if len(np.unique(values)) > 1:
self._transforms += ["weekday"]
new_column = column + "_WeekDay"
self._new_columns += [new_column]
values = X[column].dt.dayofyear
if len(np.unique(values)) > 1:
self._transforms += ["dayofyear"]
new_column = column + "_DayOfYear"
self._new_columns += [new_column]
values = X[column].dt.hour
if len(np.unique(values)) > 1:
self._transforms += ["hour"]
new_column = column + "_Hour"
self._new_columns += [new_column]
values = (X[column] - self._min_datetime).dt.days
if len(np.unique(values)) > 1:
self._transforms += ["days_diff"]
new_column = column + "_Days_Diff_To_Min"
self._new_columns += [new_column]
def transform(self, X):
column = self._old_column
if "year" in self._transforms:
new_column = column + "_Year"
X[new_column] = X[column].dt.year
if "month" in self._transforms:
new_column = column + "_Month"
X[new_column] = X[column].dt.month
if "day" in self._transforms:
new_column = column + "_Day"
X[new_column] = X[column].dt.day
if "weekday" in self._transforms:
new_column = column + "_WeekDay"
X[new_column] = X[column].dt.weekday
if "dayofyear" in self._transforms:
new_column = column + "_DayOfYear"
X[new_column] = X[column].dt.dayofyear
if "hour" in self._transforms:
new_column = column + "_Hour"
X[new_column] = X[column].dt.hour
if "days_diff" in self._transforms:
new_column = column + "_Days_Diff_To_Min"
X[new_column] = (X[column] - self._min_datetime).dt.days
X.drop(column, axis=1, inplace=True)
return X
def to_json(self):
data_json = {
"new_columns": list(self._new_columns),
"old_column": self._old_column,
"min_datetime": str(self._min_datetime),
"transforms": list(self._transforms),
}
return data_json
def from_json(self, data_json):
self._new_columns = data_json.get("new_columns", None)
self._old_column = data_json.get("old_column", None)
d = data_json.get("min_datetime", None)
self._min_datetime = None if d is None else pd.to_datetime(d)
self._transforms = data_json.get("transforms", [])
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_algorithms/test_linear.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import os
import tempfile
import unittest
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from sklearn import datasets
from supervised.algorithms.linear import LinearAlgorithm, LinearRegressorAlgorithm
from supervised.utils.metric import Metric
class LinearRegressorAlgorithmTest(unittest.TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
cls.X, cls.y = datasets.make_regression(
n_samples=100, n_features=5, n_informative=4, shuffle=False, random_state=0
)
def test_reproduce_fit(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "mse"})
params = {"seed": 1, "ml_task": "regression"}
prev_loss = None
for _ in range(3):
model = LinearRegressorAlgorithm(params)
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = model.predict(self.X)
loss = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
if prev_loss is not None:
assert_almost_equal(prev_loss, loss)
prev_loss = loss
class LinearAlgorithmTest(unittest.TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
cls.X, cls.y = datasets.make_classification(
n_samples=100,
n_features=5,
n_informative=4,
n_redundant=1,
n_classes=2,
n_clusters_per_class=3,
n_repeated=0,
shuffle=False,
random_state=0,
)
def test_reproduce_fit(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "logloss"})
params = {"seed": 1, "ml_task": "binary_classification"}
prev_loss = None
for _ in range(3):
model = LinearAlgorithm(params)
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = model.predict(self.X)
loss = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
if prev_loss is not None:
assert_almost_equal(prev_loss, loss)
prev_loss = loss
def test_fit_predict(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "logloss"})
params = {"ml_task": "binary_classification"}
la = LinearAlgorithm(params)
la.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = la.predict(self.X)
self.assertTrue(metric(self.y, y_predicted) < 0.6)
def test_copy(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "logloss"})
model = LinearAlgorithm({"ml_task": "binary_classification"})
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = model.predict(self.X)
loss = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
model2 = LinearAlgorithm({})
model2 = model.copy()
self.assertEqual(type(model), type(model2))
y_predicted = model2.predict(self.X)
loss2 = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
assert_almost_equal(loss, loss2)
def test_save_and_load(self):
metric = Metric({"name": "logloss"})
model = LinearAlgorithm({"ml_task": "binary_classification"})
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
y_predicted = model.predict(self.X)
loss = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
filename = os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), os.urandom(12).hex())
model.save(filename)
model2 = LinearAlgorithm({"ml_task": "binary_classification"})
model2.load(filename)
# Finished with the file, delete it
os.remove(filename)
y_predicted = model2.predict(self.X)
loss2 = metric(self.y, y_predicted)
assert_almost_equal(loss, loss2)
def test_is_fitted(self):
model = LinearAlgorithm({"ml_task": "binary_classification"})
self.assertFalse(model.is_fitted())
model.fit(self.X, self.y)
self.assertTrue(model.is_fitted())
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/supervised/algorithms/knn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import logging
import sklearn
from sklearn.base import ClassifierMixin, RegressorMixin
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier, KNeighborsRegressor
from supervised.algorithms.registry import (
BINARY_CLASSIFICATION,
MULTICLASS_CLASSIFICATION,
REGRESSION,
AlgorithmsRegistry,
)
from supervised.algorithms.sklearn import SklearnAlgorithm
from supervised.utils.config import LOG_LEVEL
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.setLevel(LOG_LEVEL)
KNN_ROWS_LIMIT = 1000
class KNNFit(SklearnAlgorithm):
def file_extension(self):
return "k_neighbors"
def is_fitted(self):
return (
hasattr(self.model, "n_samples_fit_")
and self.model.n_samples_fit_ is not None
and self.model.n_samples_fit_ > 0
)
def fit(
self,
X,
y,
sample_weight=None,
X_validation=None,
y_validation=None,
sample_weight_validation=None,
log_to_file=None,
max_time=None,
):
rows_limit = self.params.get("rows_limit", KNN_ROWS_LIMIT)
if X.shape[0] > rows_limit:
X1, _, y1, _ = train_test_split(
X, y, train_size=rows_limit, stratify=y, random_state=1234
)
self.model.fit(X1, y1)
else:
self.model.fit(X, y)
@property
def _classes(self):
# Returns the unique classes based on the fitted model
if hasattr(self.model, "classes_"):
return self.model.classes_
else:
return None
class KNeighborsAlgorithm(ClassifierMixin, KNNFit):
algorithm_name = "k-Nearest Neighbors"
algorithm_short_name = "Nearest Neighbors"
def __init__(self, params):
super(KNeighborsAlgorithm, self).__init__(params)
logger.debug("KNeighborsAlgorithm.__init__")
self.library_version = sklearn.__version__
self.max_iters = 1
self.model = KNeighborsClassifier(
n_neighbors=params.get("n_neighbors", 3),
weights=params.get("weights", "uniform"),
algorithm="kd_tree",
n_jobs=params.get("n_jobs", -1),
)
class KNeighborsRegressorAlgorithm(RegressorMixin, KNNFit):
algorithm_name = "k-Nearest Neighbors"
algorithm_short_name = "Nearest Neighbors"
def __init__(self, params):
super(KNeighborsRegressorAlgorithm, self).__init__(params)
logger.debug("KNeighborsRegressorAlgorithm.__init__")
self.library_version = sklearn.__version__
self.max_iters = 1
self.model = KNeighborsRegressor(
n_neighbors=params.get("n_neighbors", 3),
weights=params.get("weights", "uniform"),
algorithm="ball_tree",
n_jobs=params.get("n_jobs", -1),
)
knn_params = {"n_neighbors": [3, 5, 7], "weights": ["uniform", "distance"]}
default_params = {"n_neighbors": 5, "weights": "uniform"}
additional = {"max_rows_limit": 100000, "max_cols_limit": 100}
required_preprocessing = [
"missing_values_inputation",
"convert_categorical",
"datetime_transform",
"text_transform",
"scale",
"target_as_integer",
]
AlgorithmsRegistry.add(
BINARY_CLASSIFICATION,
KNeighborsAlgorithm,
knn_params,
required_preprocessing,
additional,
default_params,
)
AlgorithmsRegistry.add(
MULTICLASS_CLASSIFICATION,
KNeighborsAlgorithm,
knn_params,
required_preprocessing,
additional,
default_params,
)
AlgorithmsRegistry.add(
REGRESSION,
KNeighborsRegressorAlgorithm,
knn_params,
required_preprocessing,
additional,
default_params,
)
```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/tests_automl/test_automl_time_constraints.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```python
import shutil
import time
import unittest
from supervised import AutoML
from supervised.tuner.time_controller import TimeController
class AutoMLTimeConstraintsTest(unittest.TestCase):
automl_dir = "automl_tests"
def tearDown(self):
shutil.rmtree(self.automl_dir, ignore_errors=True)
def test_set_total_time_limit(self):
model_type = "Xgboost"
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir, total_time_limit=100, algorithms=[model_type]
)
automl._time_ctrl = TimeController(
time.time(), 100, None, ["simple_algorithms", "not_so_random"], "Xgboost"
)
time_spend = 0
for i in range(12):
automl._start_time -= 10
automl._time_ctrl.log_time(f"Xgboost_{i}", model_type, "not_so_random", 10)
if automl._time_ctrl.enough_time(model_type, "not_so_random"):
time_spend += 10
self.assertTrue(time_spend < 100)
def test_set_model_time_limit(self):
model_type = "Xgboost"
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir, model_time_limit=10, algorithms=[model_type]
)
automl._time_ctrl = TimeController(
time.time(), None, 10, ["simple_algorithms", "not_so_random"], "Xgboost"
)
for i in range(12):
automl._time_ctrl.log_time(f"Xgboost_{i}", model_type, "not_so_random", 10)
# should be always true
self.assertTrue(automl._time_ctrl.enough_time(model_type, "not_so_random"))
def test_set_model_time_limit_omit_total_time(self):
model_type = "Xgboost"
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=10,
model_time_limit=10,
algorithms=[model_type],
)
automl._time_ctrl = TimeController(
time.time(), 10, 10, ["simple_algorithms", "not_so_random"], "Xgboost"
)
for i in range(12):
automl._time_ctrl.log_time(f"Xgboost_{i}", model_type, "not_so_random", 10)
# should be always true
self.assertTrue(automl._time_ctrl.enough_time(model_type, "not_so_random"))
def test_enough_time_to_train(self):
model_type = "Xgboost"
model_type_2 = "LightGBM"
model_type = "Xgboost"
automl = AutoML(
results_path=self.automl_dir,
total_time_limit=10,
model_time_limit=10,
algorithms=[model_type, model_type_2],
)
automl._time_ctrl = TimeController(
time.time(),
10,
10,
["simple_algorithms", "not_so_random"],
[model_type, model_type_2],
)
for i in range(5):
automl._time_ctrl.log_time(f"Xgboost_{i}", model_type, "not_so_random", 1)
# should be always true
self.assertTrue(automl._time_ctrl.enough_time(model_type, "not_so_random"))
for i in range(5):
automl._time_ctrl.log_time(
f"LightGBM_{i}", model_type_2, "not_so_random", 1
)
# should be always true
self.assertTrue(
automl._time_ctrl.enough_time(model_type_2, "not_so_random")
)
def test_expected_learners_cnt(self):
automl = AutoML(results_path=self.automl_dir)
automl._validation_strategy = {"k_folds": 7, "repeats": 6}
self.assertEqual(automl._expected_learners_cnt(), 42)
automl._validation_strategy = {"k_folds": 7}
self.assertEqual(automl._expected_learners_cnt(), 7)
automl._validation_strategy = {}
self.assertEqual(automl._expected_learners_cnt(), 1)
```